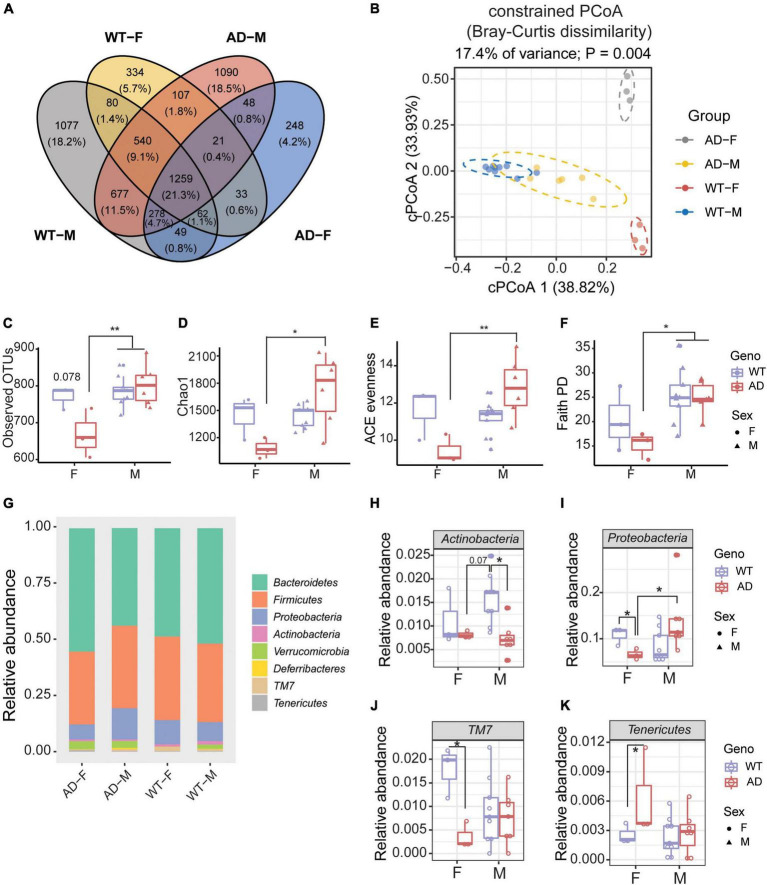
FIGURE 4.
Sex differences exhibited in the gut microbiome of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) mice. (A) Venn diagram depicting the unique and shared operation taxonomic units (OTUs) between males and females of 2xTg AD and wild-type (WT) mice. (B) Beta diversity is represented by constrained principal coordinate analysis (cPCoA) analysis using genotype as the constraining variable and ordinated with Jaccard dissimilarity. (C,D) The richness of gut microbiome diversity is represented by observed OTUs (C) and Chao1 (D) indices (n = 3–6). (E,F) The evenness of gut microbiome diversity is represented by ACE evenness (E) and faith PD (F) (n = 3–6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons. (G) Microbiome composition at the phylum level (n = 3–6). (H–K) The relative abundance of phyla of male and female mice in both 2xTg AD and WT groups (n = 3–6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01; two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons. Data are shown as all samples with a boxplot. F, females; M, males. AD, 6 males and 3 females; WT, 9 males and 3 females; all mice were 12-month-old.