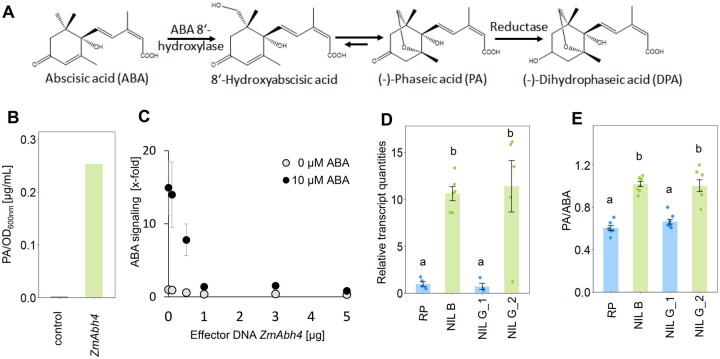
Figure 2.
ZmAbh4 encodes an ABA 8′-hydroxylase that modulates ABA catabolism in the maize leaf. A, Main catabolic pathway of ABA. B, ABA 8′-hydroxylase encoded by the NIL B ZmAbh4 allele converts ABA to PA, as shown by ZmAbh4 expression in yeast. Concentration of PA in the supernatant of the yeast culture was normalized to the OD600nm of the culture at harvest. In the control (yeast without ZmAbh4 expression), PA was below the detection limit. C, ABA signaling in Arabidopsis protoplasts that were transiently transfected with varying amounts of ZmAbh4 (NIL B allele) effector DNA with equal amounts of total DNA (5 µg, adjusted with vector control) and incubated in the presence or absence of 10 µM ABA. ABA signaling is given as ABA-dependent luciferase induction relative to the value without exogenous ABA and effector DNA. Means ± SE (n = 6 transfections of 105 protoplasts each). Transfection with 3 µg cDNA of the RP and NIL B alleles of ZmAbh4 resulted in equal reductions in ABA signaling for both alleles. D, Transcript levels of ZmAbh4 in the leaves of plants at the V5 stage, measured with primers spanning intron 4. Means ± SE (n = 4–6 plants). E, Ratio of leaf 5 PA and ABA concentrations in the last developed leaves at the V5 stage. Means ± SE (n = 7–8 plants). Significant differences (LSD test) in (D) and (E) are marked with different letters.