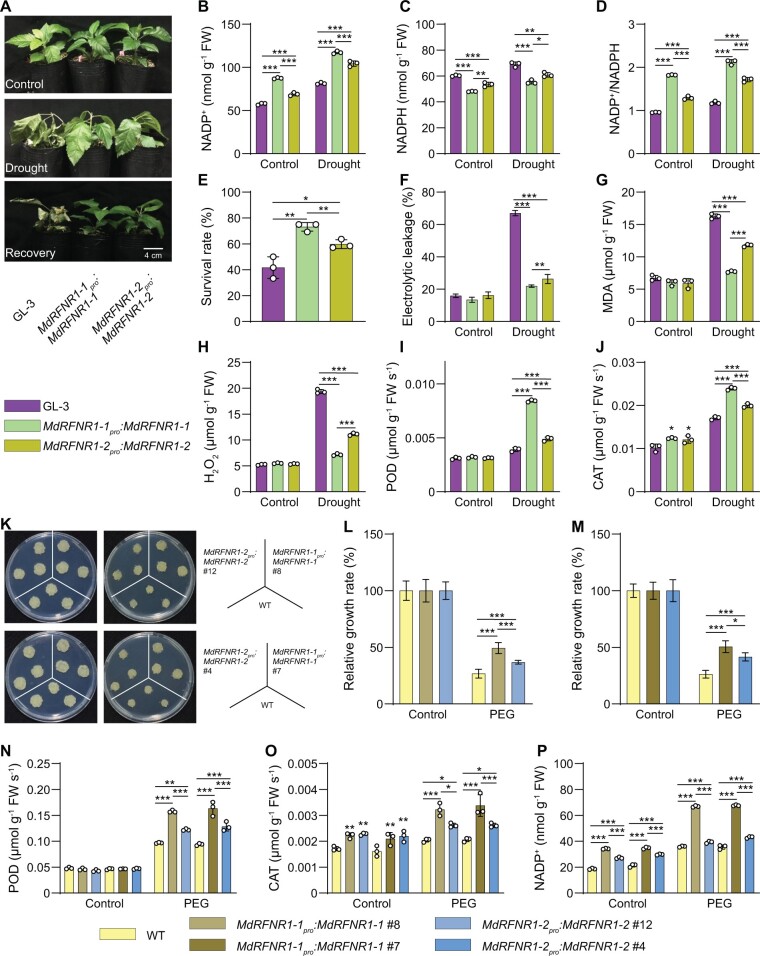
Figure 6.
The MdRFNR1-1 allele plays a more important role than MdRFNR1-2 in drought stress tolerance. A, Morphology of GL-3 and transgenic plants carrying MdRFNR1-1pro:MdRFNR1-1 or MdRFNR1-2pro:MdRFNR1-2 under control and drought conditions. Water was withheld from 1.5-month-old plants for 15 days, followed by recovery for 7 days. B–D, Contents of NADP+ (B), NADPH (C), and NADP+/NADPH ratio (D) of GL-3 and transgenic plants carrying MdRFNR1-1pro:MdRFNR1-1 or MdRFNR1-2pro:MdRFNR1-2 under control and drought treatment. E, The survival rates of plants shown in (A). F–J, Leaf ion leakage (F), MDA (G) and H2O2 (H) contents, POD (I) and CAT (J) activities of GL-3, and transgenic plants carrying MdRFNR1-1pro:MdRFNR1-1 or MdRFNR1-2pro:MdRFNR1-2 under control and drought treatment. K, Morphology of WT and transgenic calli after 20 days on MS medium (left) or MS medium supplemented with PEG (right). L–M, Relative growth rates of WT and transgenic calli carrying MdRFNR1-1pro:MdRFNR1-1 or MdRFNR1-2pro:MdRFNR1-2. N–P, POD (N) and CAT (O) activities and NADP+ contents (P) of WT and transgenic calli carrying MdRFNR1-1pro:MdRFNR1-1 or MdRFNR1-2pro:MdRFNR1-2 under control and PEG treatment. Error bars indicate sd, n = 3 in (B, C, D, G, H, I, J, N, O, and P), n = 36 in (E, 36 plants were used and divided into three biological replications), n = 8 in (F), and n = 9 in (L and M). Asterisks indicate significant differences between the transgenic lines and GL-3 plants in each group (control and drought treatment). One-way ANOVA (Tukey’s test) was performed and statistically significant differences are indicated by *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, or ***P ≤ 0.001.