Figure 1. Examples of endogenous and exogenous sources of DNA damage encountered by bacteria.
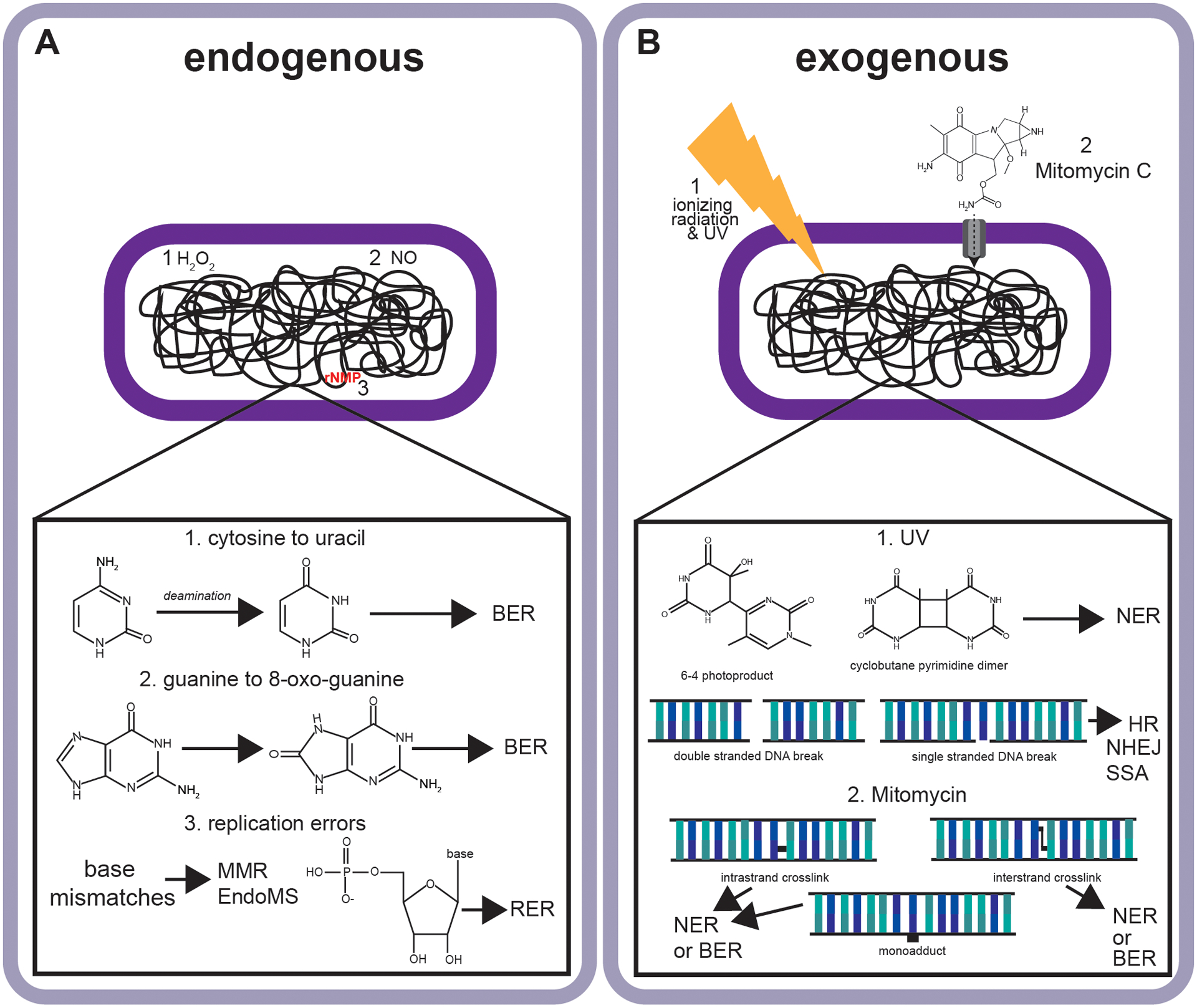
(A) Endogenous sources of damage or errors including base deamination (1), oxidative DNA damage (2), and DNA replication errors including base pairing errors and ribonucleotide errors (3). (B) Examples of exogenous sources of damage including UV cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (1) and 6–4 photoproducts (1) as well as the uptake of antimicrobial compounds including mitomycin C which damage DNA forming cross-links, and a monoadduct (3). Abbreviations include base excision repair (BER), nucleotide excision repair (NER), homologous recombination (HR), non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ), single strand annealing (SSA), mismatch repair (MMR) and ribonucleotide excision repair (RER).
