Figure 3. Azinomycin B and nitrogen mustard interstrand crosslink repair.
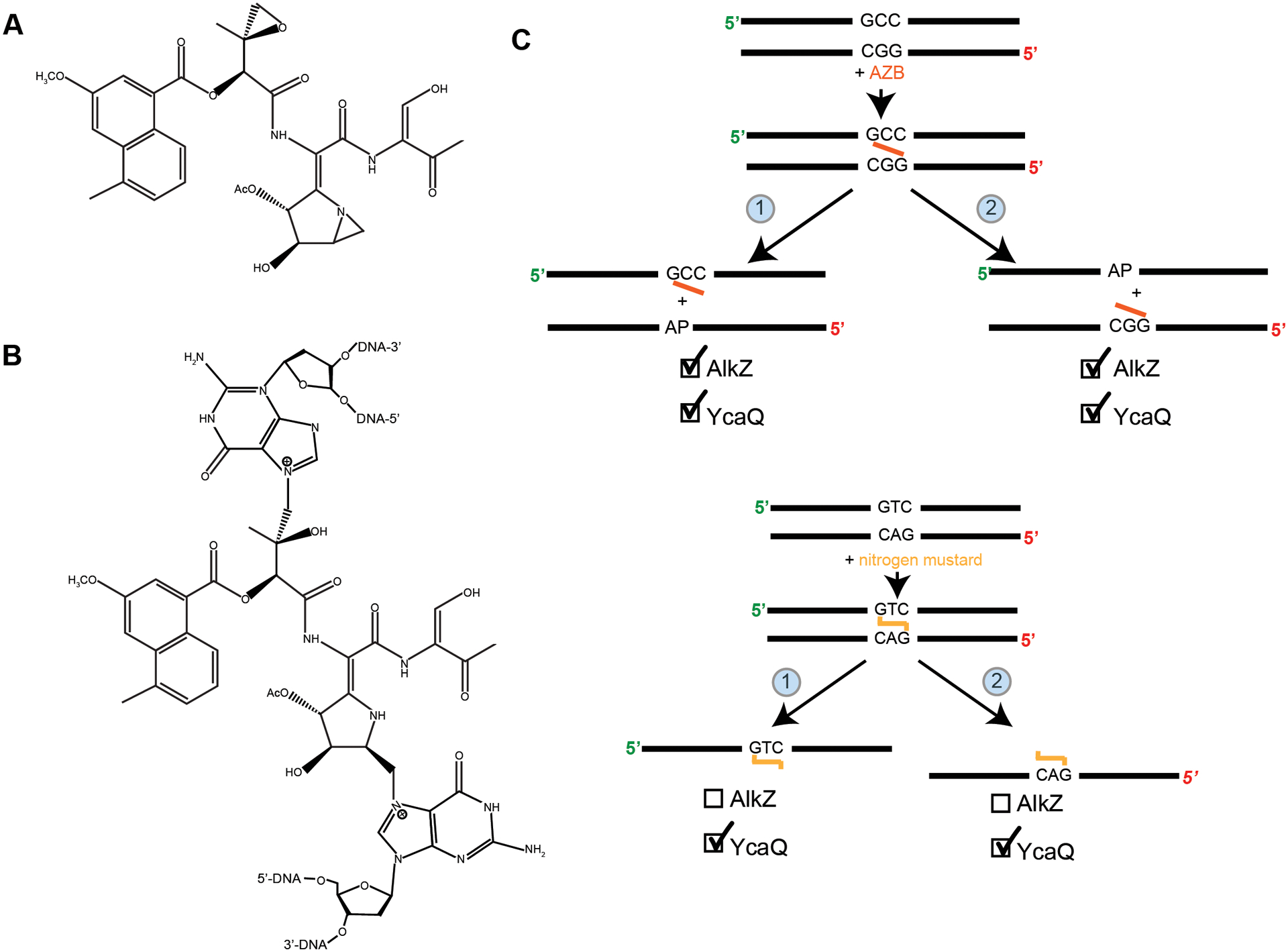
(A) Structure of azinomycin B (AZB) (adapted from71). (B) Structure of interstrand crosslink formed by azinomycin B (adapted from71). (C) Top: AZB asymmetric crosslinked substrate and possible unhooking products. AlkZ was shown to unhook crosslinks from both sides with preference toward the GGC side (product 1). YcaQ was shown to unhook the crosslink from both sides with slight preference toward unhooking the CGG side (product 2). Bottom: Nitrogen mustard symmetric crosslinked substrate and possible unhooking products. YcaQ was able to unhook both sides of the crosslink, while AlkZ showed no activity71.
