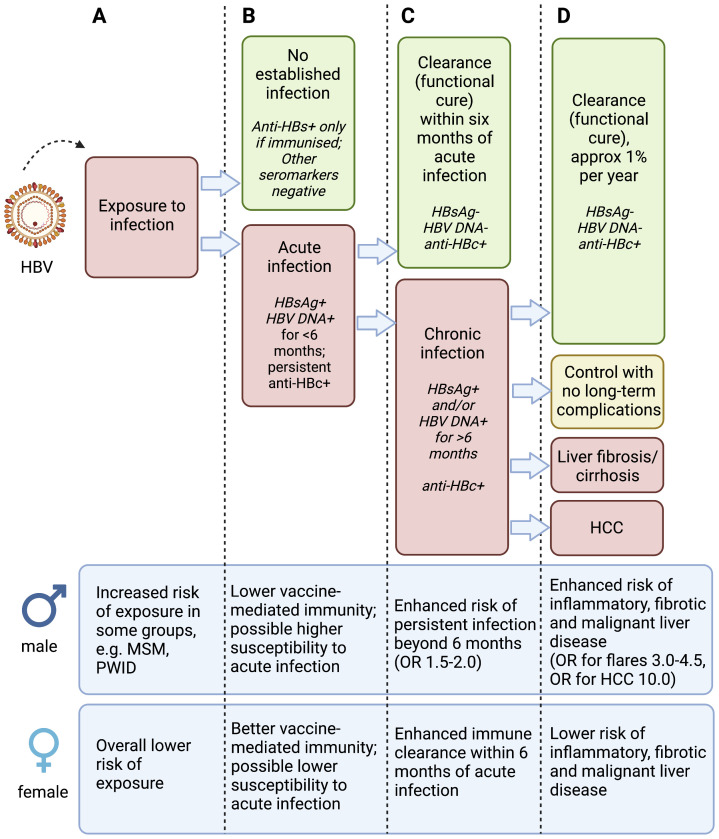
Figure 1. Schematic to illustrate phases of hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection and relevant sex differences.
Infection is considered according to exposure to the virus (column A), acute infection (column B), chronic infection (column C) and liver disease (column D), with data for males and females presented at the bottom of each column. Anti-HBs – antibody to HBV surface antigen; HBsAg – Hepatitis B virus surface antigen; Anti-HBc – antibody to HBV core protein; HCC – hepatocellular carcinoma; MSM – men who have sex with men; PWID – people who inject drugs. OR (odds ratio) for males is presented based on females as the reference group. There is varied evidence for the specific observations presented in this figure, and the magnitude of increased risk in males varies between populations and settings. Figure created with BioRender.com, with licence to publish.