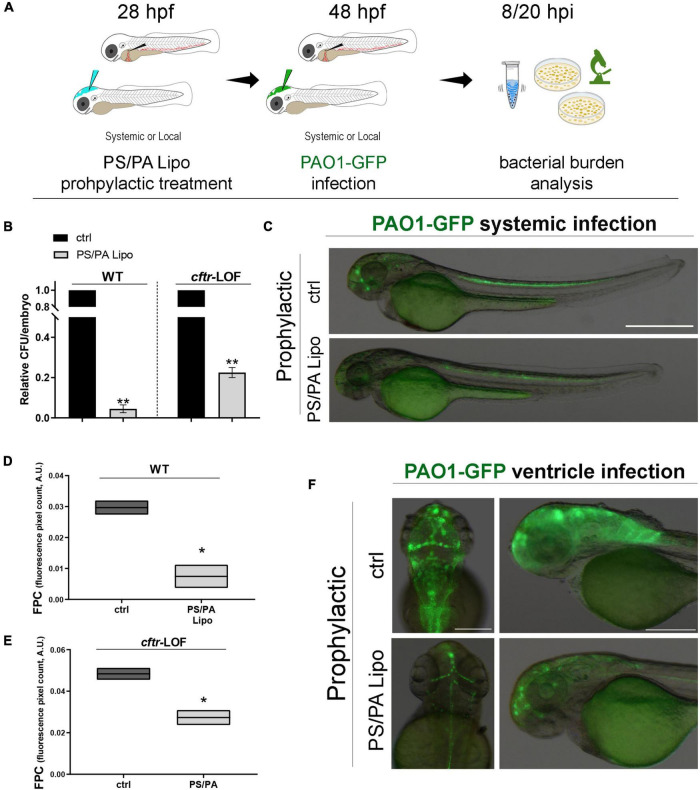
FIGURE 1.
Antimicrobial activity of phosphatidylserine/phosphatidic acid (PS/PA) liposome prophylactic administration in wild-type (WT) and cftr-LOF zebrafish embryos. (A) Schematic representation of PS/PA liposome prophylactic treatment. Zebrafish embryos were treated with PS/PA liposome at 28 hpf, then systemically or locally infected with 100–300 CFU PAO1-GFP at 48 hpf and analyzed for bacterial burden at 8 or 20 h post infection. (B) Bacterial load (relative CFU/embryo) in systemically infected WT and cftr-LOF embryos, control (ctrl), and PS/PA liposome treated at 8 hpi. Results are presented as mean ± SEM. (C) Representative images of PAO1-GFP systemic bacterial infection in ctrl and PS/PA liposome treated embryos. (D,E) Quantitative analysis (fluorescence pixel count) of PAO1-GFP locally injected in the close cavity of the hindbrain ventricle of WT and cftr-LOF embryos, control (ctrl) and PS/PA liposome treated. The mean and the min to max values of at least two independent experiments (3–10 embryos/treatment) were reported on floating bars. (F) Representative images of PAO1-GFP ventricle bacterial infection in ctrl and PS/PA liposome treated embryos. Statistical significance was assessed by unpaired Student’s t test: **p < 0.01; *p < 0.05. Scale bar indicates 500 μm in panel (C) and 200 μm (dorsal) and 150 μm (lateral) in panel (F).