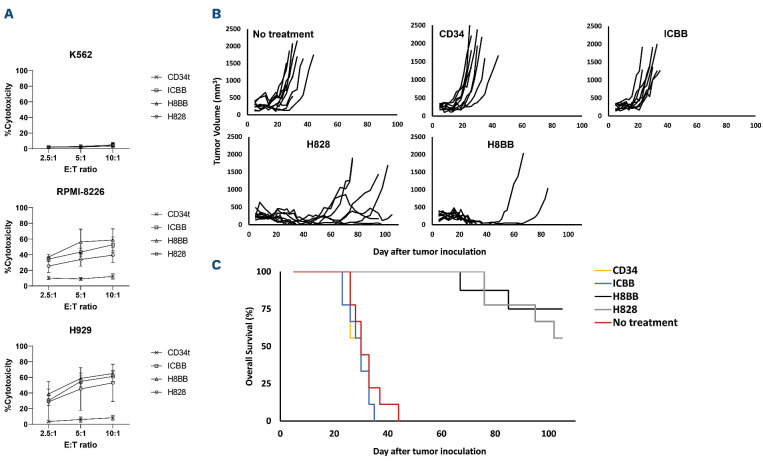
Figure 5.
BCMA chimeras mediate anti-tumor cytotoxic activity in vitro and in vivo. (A) BCMA CAR or CD34t (control) transduced T cells were co-cultured with CFSE-labeled tumor cells at the indicated effector to target (E:T) ratios. After 4 hours, propidium iodide (PI) was added and the cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Cytotoxicity was calculated based on the proportion of CFSE+/PI+ population out of the total CFSE+ population. These results are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of 3 independent experiments with 3 different donors and the difference between the BCMA-CARs and CD34t populations was found statistically significant (P<0.05, calculated using a Student’s paired t-test). (B) In vivo function of BCMA-CAR-T cells. NSG xenografts (n=8-9 per group) were inoculated H929 myeloma cells. One week following tumor inoculation, the mice were intravenously injected either with 15x106 BCMA-CAR+ or with CD34t-transduced control cells. Tumor volume was measured in a blinded fashion using a caliper and calculated using the following formula: (D×d2)×Π/6, where D is the largest tumor diameter and d its perpendicular one. (C) Overall survival analysis. The difference in the average survival of the H828 and H8BB groups compared to the no-treatment or control groups was found statistically significant (P<1e-4, using a logrank analysis). BCMA: B-cell maturation antigen; CAR: chimeric antigen.