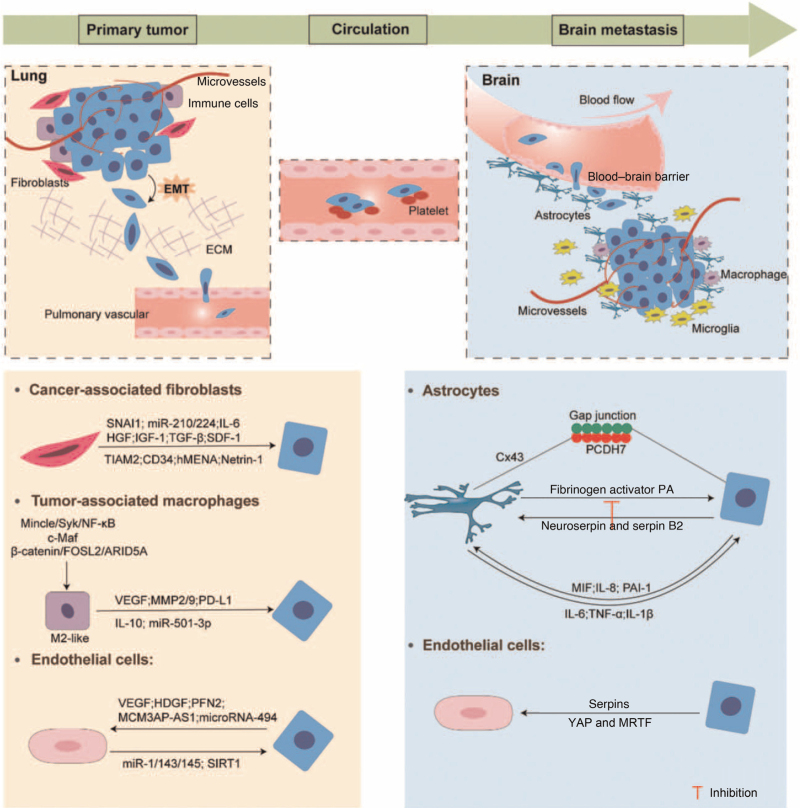
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the stages of the formation of LCBM and interactions between TME and tumor cells. ARID5A: AT-rich interaction domain 5A; Cx43: Connexin 43; ECM: Extracellular matrix; EMT: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; FOSL2: Fos-like antigen 2; HDGF: Hepatoma-derived growth factor; HGF: Hepatocyte growth factor; hMENA: human mammalian ENA; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; IL: Interleukin; LCBM: Lung cancer brain metastasis; MCM3AP-AS1: lncRNA MCM3AP antisense RNA 1; MIF: Migration inhibitory factor; miR: MicroRNA; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinases; MRTF: Myocardin-related transcription factor; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa-B; PA: Plasminogen activator; PAI-1: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; PCDH7: Pro-calmodulin 7; PD-L1: Programmed cell death-ligand 1; PFN2: Profilin 2; SDF-1: Stromal cell-derived factor-1; SIRT1: Sirtuin 1; SNAI1: Snail 1; TGF-β: Transforming growth factor-β; TIAM2: T-cell lymphoma invasion and metastasis 2; TME: Tumor microenvironment; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; YAP: Yes-associated protein.