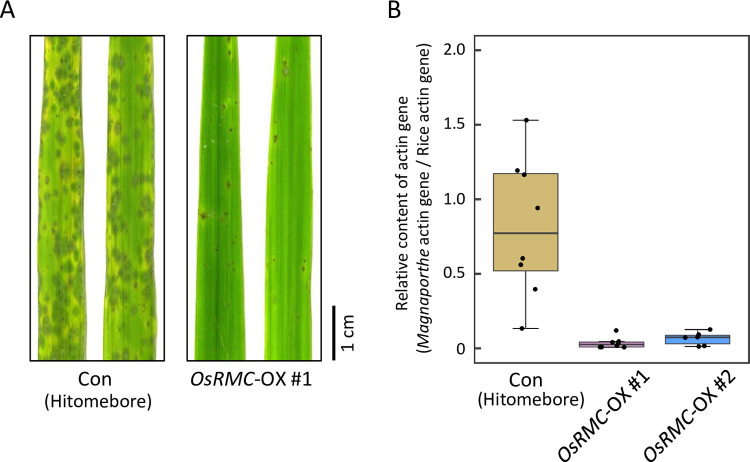
Fig 5. OsRMC-overexpressing rice plants show enhanced resistance against M. oryzae.
(A) Rice leaves of wild-type (Hitomebore) control (Con) and OsRMC-overexpressing (OsRMC-OX) lines 4 days after inoculation of M. oryzae (Ken53-33, 1.5 X 106 conidia) inoculation. The M. oryzae infection test was conducted using wild-type control (n = 10) and OsRMC-OX (#1 [n = 6] and #2 [n = 6]) lines. (B) M. oryzae infection is suppressed in OsRMC-OX lines. The amount of M. oryzae fungal mass in rice leaf was monitored by quantifying the ratio of M. oryzae genomic DNA to rice genomic DNA, determined by qPCR of the respective actin genes. The average ΔΔCt value in wild-type control lines was defined as the unit for the ratio. Data are means ± SD of independent determinations. Double asterisks indicate a significant difference at P < 0.01, respectively, according to Student’s t-test.