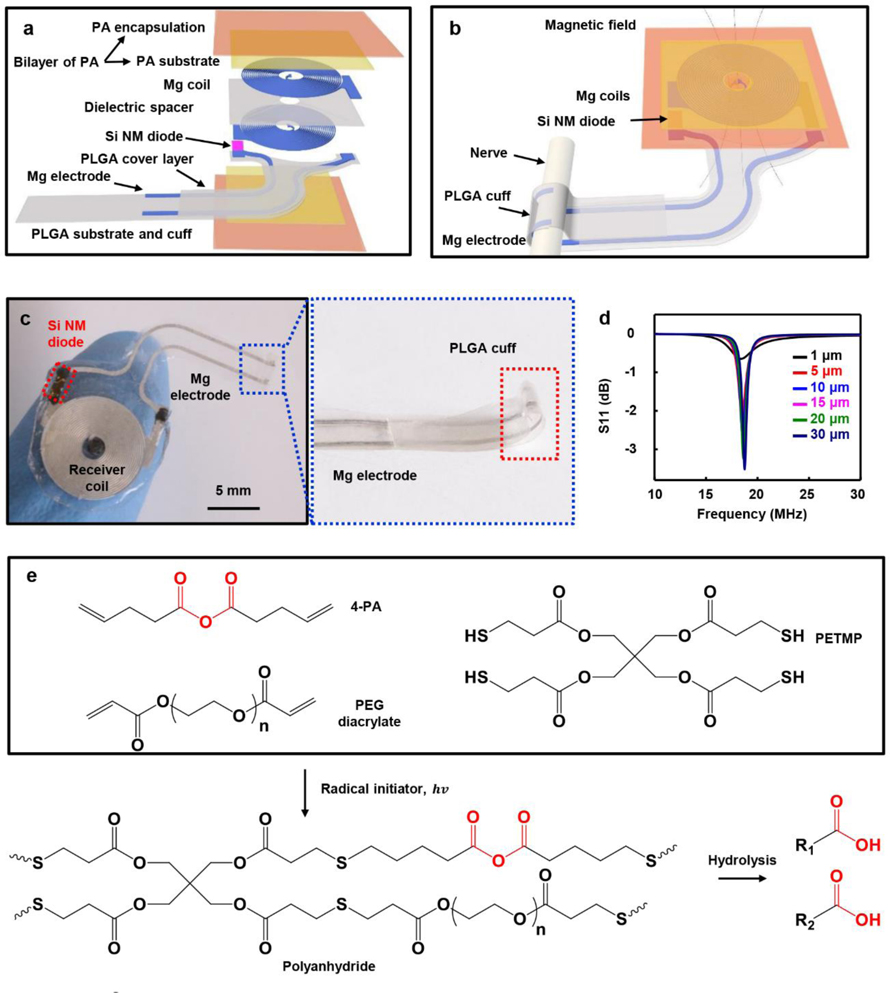
Figure 1.
Controlled-bioresorbable, wireless electrical stimulator. a) Exploded view schematic illustration of the device structure. b) Schematic illustration of the complete device, with nerve cuff interface. c) Image of a wireless electrical stimulator and magnified view of the hot-pressed PLGA cuff and Mg electrode. d) Electromagnetic simulation of the radio frequency behavior of the wireless electrical stimulator with various Mg thickness. e) Chemical components use to form the polyanhydride (PA) via UV initiated thiol-ene click reactions and the hydrolysis of anhydride. 4-PA: 4-pentenoic anhydride, PEG diacrylate: poly (ethylene glycol) diacrylate, PETMP: pentaerythritol tetrakis(3-mercaptopropionate).