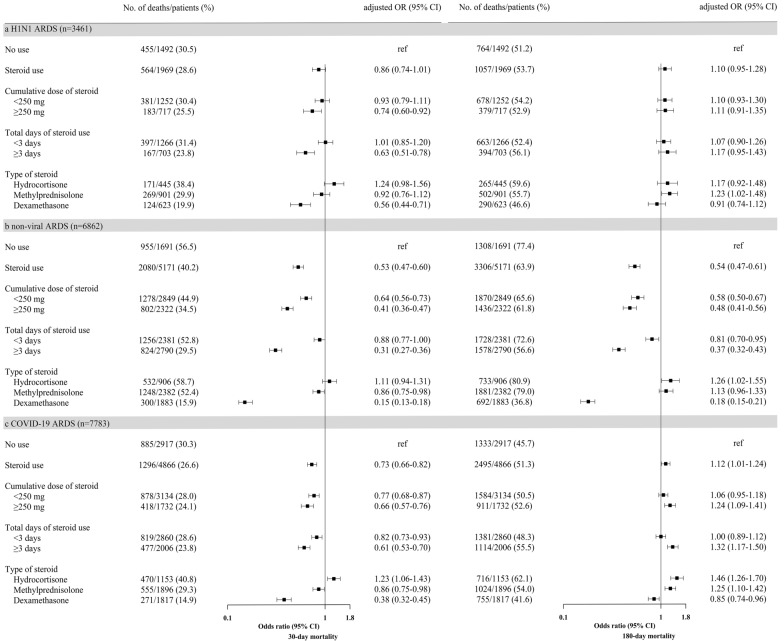
Fig. 1.
Associations between corticosteroid use or dosage of, duration of treatment with, and type of steroids and 30- and 180-day mortality in a H1N1, b non-viral, or c COVID-19 ARDS. The numbers and percentages of patients who died according to each risk factor and the resulting odds ratios. For steroid use, the odds ratios were adjusted for age, sex, Charlson Comorbidity Index, immunosuppression, hospital type, organ dysfunction, steroid use, neuromuscular blocking agent use, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. For cumulative dose of steroid, total days of steroid use, and type of steroids, the odds ratios were adjusted for age, sex, Charlson Comorbidity Index, immunosuppression, hospital type, organ dysfunction, neuromuscular blocking agent use, and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. ARDS acute respiratory distress syndrome; COVID-19 coronavirus disease 2019; H1N1 2009 influenza A