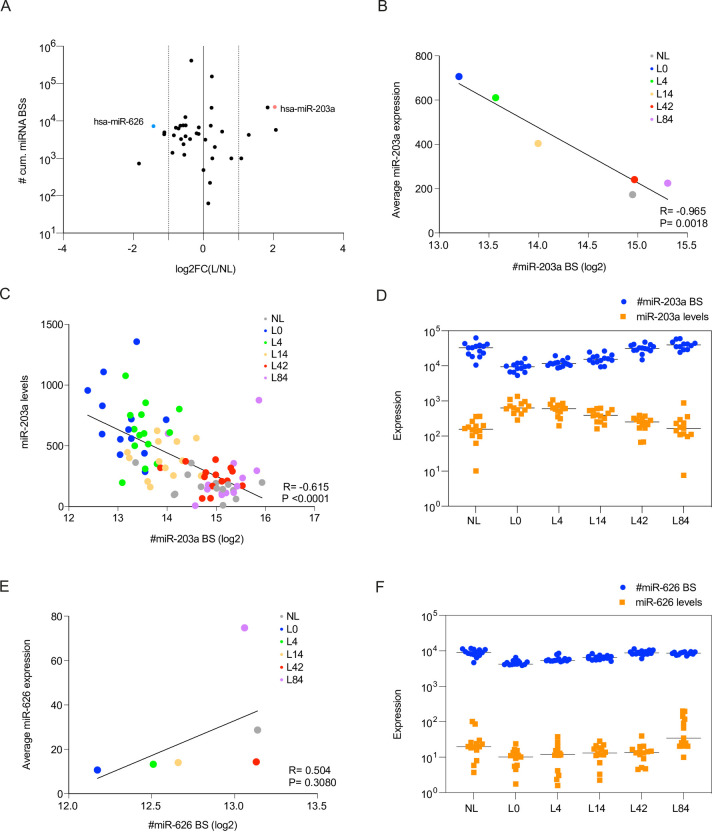
Fig 5. MiR-203a-3p expression changes correlate with total number of seed sites on most abundant circRNAs in psoriasis during secukinumab treatment.
(A) Estimated number of total miRNA binding sites (BSs) for the most abundant circRNAs in psoriasis (on log10 scale) relative to the log2FC between lesional and non-lesional skin. The number of miRNA BSs was estimated by the sum over the product of all circRNAs with predicted unique miRNA BSs and their respective average circRNA expression level at the time point. (B-C) Correlation of average (B) or patient-specific (C) miR-203a-3p expression over the course of treatment with a proxy for the total number of miR-203a BSs present in the most abundant circRNAs in psoriasis (see description for estimation in A). Simple linear regression was used for correlation between average miR-203a-3p expression (y-axis) and the log2-transformed values of the predicted number of miR-203a BSs across all circRNAs (x-axis). (D) Opposing absolute changes (on log10 scale) in miR-203a-3p expression levels (yellow) and estimated number of circRNA-specific miR-203a seed sites during secukinumab treatment. (E) Correlation of average miR-626 expression over the course of treatment with a proxy for the total number of miR-626 BSs present in the most abundant circRNAs in psoriasis (see description for estimation in A). Simple linear regression was used for establishing the correlation between average miR-626 expression (y-axis) and the log2-transformed values of the predicted number of miR-626 BSs across all circRNAs (x-axis). (F) Matching absolute expression changes (on log10 scale) in miR-626 expression levels (yellow) and estimated number of circRNA-specific miR-626 seed sites during secukinumab treatment.