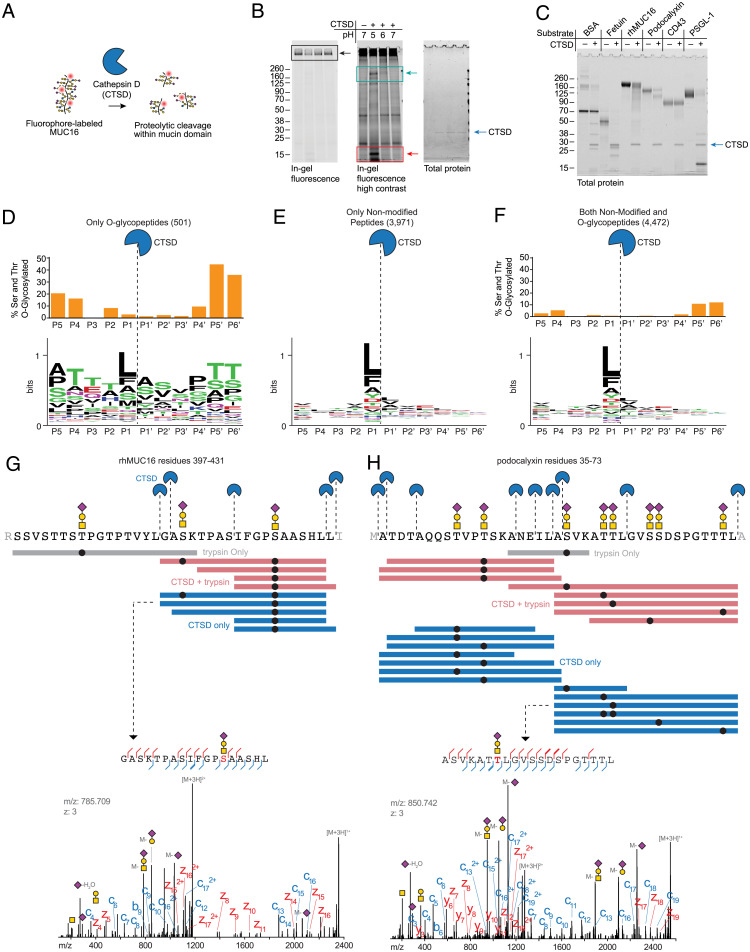
Fig. 3.
Purified human cathepsin D cleaves MUC16 and other mucins within their densely glycosylated mucin domains. (A) Schematic of mucin proteolysis assay with lysosomal cathepsin D purified from human liver. (B) A commercial preparation of cathepsin D purified from human liver (Molecular Innovations) was incubated at 50 nM with MUC16-800 at 37 °C overnight. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by in-gel fluorescence followed by Coomassie (total protein). Black boxes highlight the substrate band; cyan boxes highlight appearance of a product band between 160 and 260 kDa; red boxes highlight appearance of a product band between 8 and 15 kDa. (C) Protein substrates were incubated with 500 nM human cathepsin D at pH 5 overnight at 37 °C. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE, then stained with Coomassie for total protein. (D–F) Cleavage motif of cathepsin D as determined by glycoproteomic analysis on the substrates shown in C (Dataset S3). WebLogo was used for logo plot generation (35). The percentage of O-glycosylated serine and threonine residues in peptide identifications resulting from CTSD-derived cleavage was determined by counting the number of modified residues at a given position relative to the total number of residues (SI Appendix, Supplementary Methods) and is shown as bar graphs above the logos for O-glycopeptides (D), nonmodified O-glycopeptides (E), and an aggregate of both (F). (G) Top: Visualization of cathepsin D cleavage sites in rhMUC16 residues 397 to 431 (see SI Appendix, Supplementary Methods for sequence). Purple diamond, sialic acid; yellow circle, galactose; yellow square, N-acetylgalactosamine; black circle, glycosylation site. Colored bars represent individual detected peptides from trypsin only, CTSD + trypsin, and CTSD only samples. Bottom: annotated spectrum for the indicated MUC16 peptide. (H) Top: visualization of cathepsin D cleavage sites in podocalyxin residues 35 to 73, represented as in E. Bottom: annotated spectrum for the indicated podocalyxin peptide.