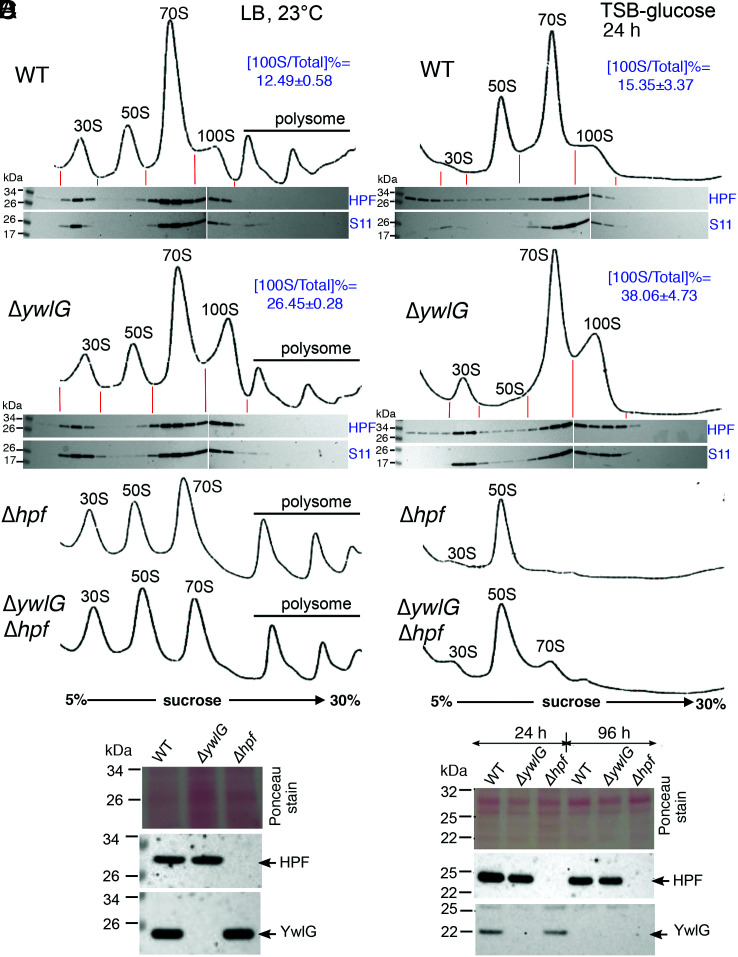
Fig. 4.
Inactivation of ywlG increases the formation of 100S ribosomes. (A and C) Ribosome sedimentation profiles of WT and its mutants. Cells were grown in LB at 23 °C until OD600 = 1.6 (A) or grown in TSB-glucose at 37 °C for 24 h (C). Crude ribosomes were extracted and subjected to 5–30% sucrose gradient fractionation (x axes), and ribosomal complexes were monitored by ultraviolet absorbance at 254 nm (y axes). Western blots show that significant amount of ribosome-free HPF was found in the WT than the ΔywlG mutant (C, Bottom). The ratios of 100S ribosome versus total mature ribosome content were quantitated according to the areas under the curve using ImageJ (n = 3, mean ± SD). The 100S ribosomes accumulate upon ywlG deletion by greater than twofold relative to the level in the WT. (B and D) Western blots showing that the levels of HPF were unaffected by ΔywlG knockout in the total lysates of LB cultures (A) and TSB-glucose cultures (D). Total proteins were resolved on a 4–12% Bis-Tris NuPAGE gel, and immunoblotting was performed with anti-YwlG (1/1,000) or anti-HPF (1/4,000).