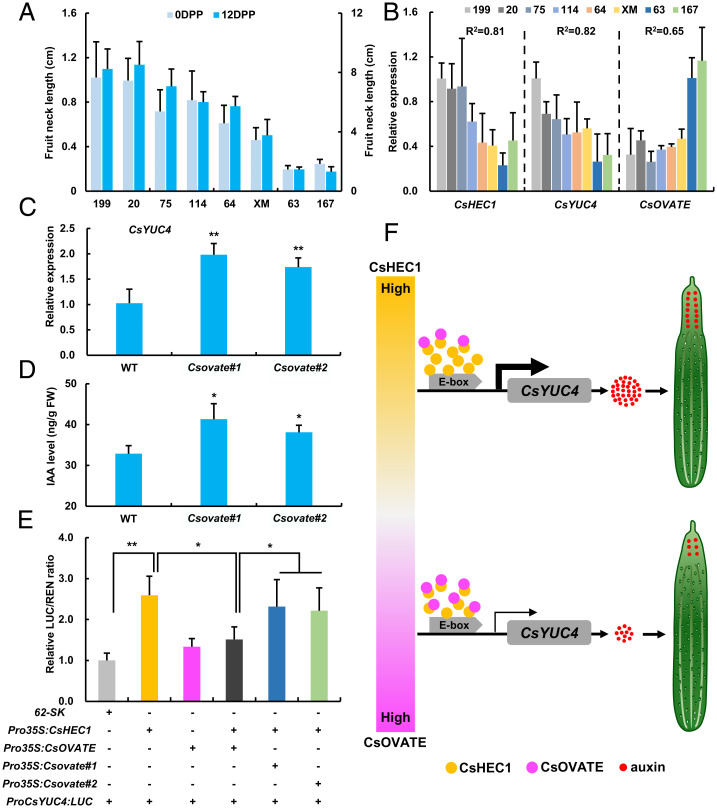
Fig. 7.
CsOVATE antagonizes CsHEC1-mediated CsYUC4 activation during fruit neck elongation in cucumber. (A) Cucumber inbred lines with different FNL at 0 and 10 DPP. (B) Expression analysis of CsHEC1, CsYUC4, and CsOVATE in different cucumber inbred lines. (C) Expression analysis of CsYUC4 in WT and Csovate mutants. (D) IAA content in the fruit necks of WT and Csovate mutants. Values are means ± SD (n = 3 in C and D). (E) Firefly luciferase and renilla reiformis luciferase activity assay in N. benthamiana leaves by coexpression of Pro35S:CsHEC1 and/or Pro35S:CsOVATE or Pro35S:Csovate#1 or Pro35S:Csovate#2 with ProCsYUC4:LUC. Values are means ± SD (n = 5). Significance analysis was calculated by Student’s t test (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). (F) The working model of CsHEC1 and CsOVATE regulating fruit neck elongation in cucumber. CsHEC1 promotes fruit neck elongation in cucumber by directly activating the expression of CsYUC4 and thus increasing auxin accumulation in the fruit neck. CsOVATE functions as a negative regulator for fruit neck elongation via interaction with CsHEC1 to attenuate the CsHEC1-mediated CsYUC4 activation, thus reducing auxin biosynthesis in the fruit neck.