Figure 3.
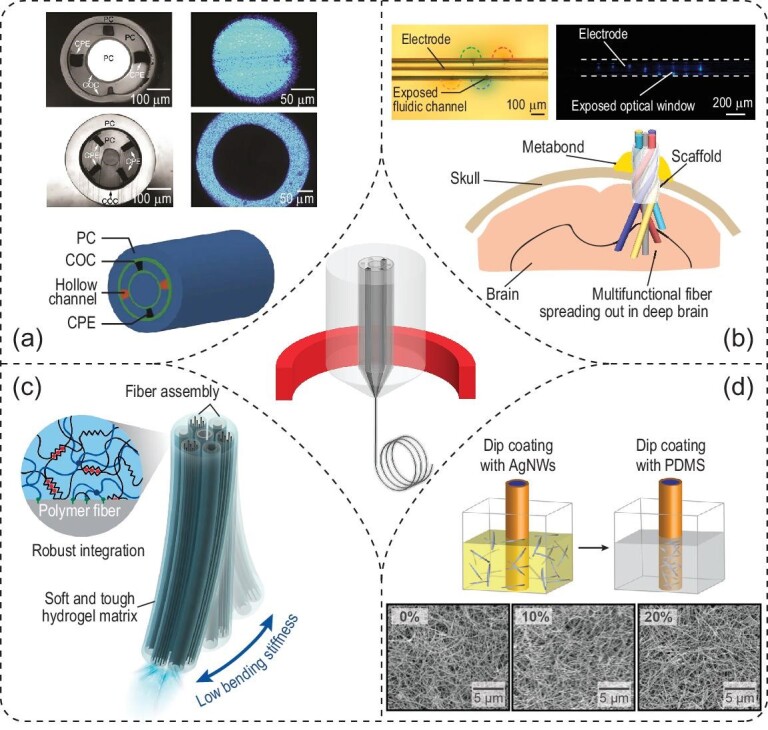
Optogenetic interfaces based on multifunctional fibers. (a) Cross-sectional photographs (top panels) and schematic (bottom panel) of multifunctional fibers. Photographs in the right column reveal light propagation in the core and outer layer of two different multifunctional fibers. Adapted with permission from [47]. Copyright 2015, Nature Publishing Group. (b) Depth-dependent (top panels) and spatially expandable (bottom panel) multifunctional fibers enable interfacing with a larger volume of the neural tissue. Adapted with permission from [51]. Copyright 2020, Nature Publishing Group. (c) Adaptive hydrogel hybrid probe incorporates fiber probes of different functions in a hydrogel matrix. Adapted with permission from [53]. Copyright 2021, Nature Publishing Group. (d) Stretchable multifunctional fibers. Top: the dip-coating process to fabricate the stretchable electrode composed of AgNWs. Bottom: scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images of the stretchable electrode reveal similar connectivity in the mesh structure under different strains. Adapted with permission from [54]. Copyright 2017, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
