Figure 7.
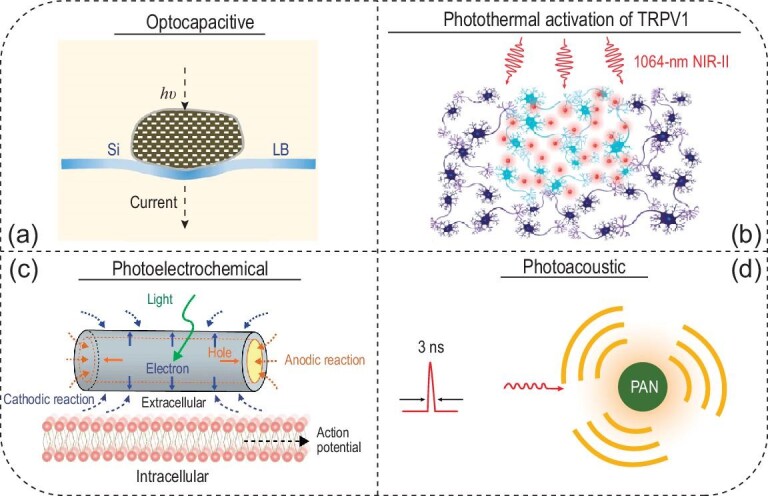
Other optical neural interfaces based on (a) optocapacitive, (b) photothermal, (c) photoelectrochemical and (d) photoacoustic effects. (a) Lipid-supported Si mesostructures convert 532-nm light into transmembrane current to depolarize neurons with high efficiency. Adapted with permission from [85]. Copyright 2016, Nature Publishing Group. (b) Macromolecular infrared nanotransducers for deep-brain stimulation (MINDS) convert 1064-nm NIR-II light into transient local heating for activating TRPV1 channels in the deep mouse brain. This approach eliminates the brain implants and head tethering for neuromodulation in freely behaving animals. (c) Coaxial p-type/intrinsic/n-type (PIN) Si nanowires (SiNWs) produce Faradaic currents to induce action potentials under 532-nm irradiation. Adapted with permission from [97]. Copyright 2018, Nature Publishing Group. (d) Photoacoustic nanotransducers (PANs) convert nanosecond 1030-nm laser pulses into acoustic waves for neuromodulation. Adapted with permission from [100]. Copyright 2020, Elsevier Inc.
