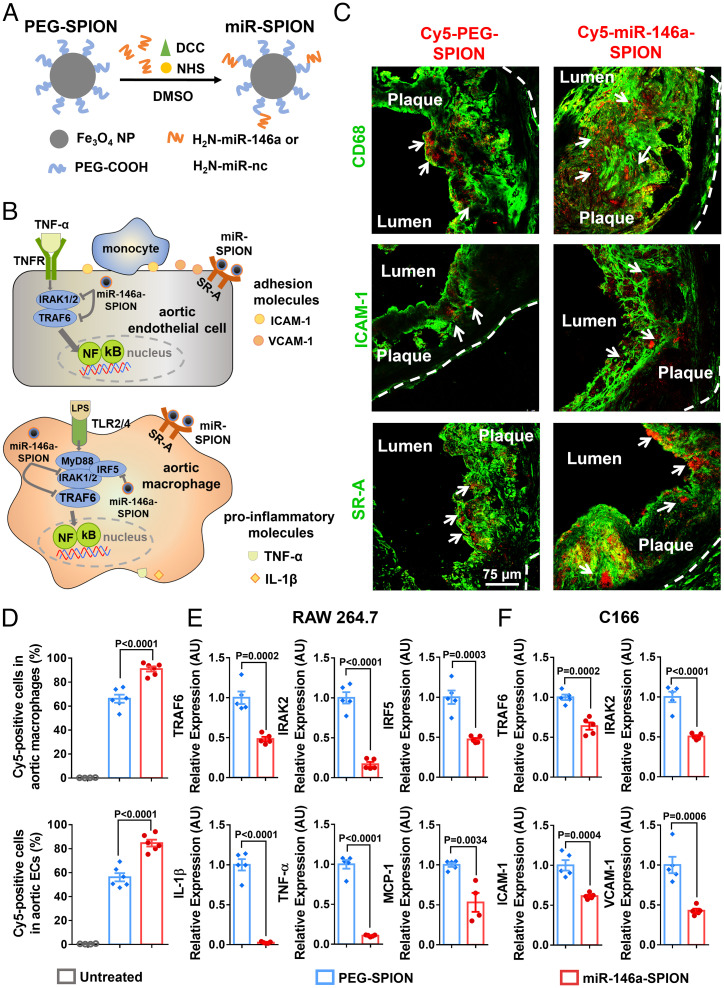
Fig. 1.
Ex vivo binding of miR-146a-SPIONs to endothelial cells and macrophages in atherosclerotic plaque and in vitro down-regulation of genes related to NF-κB pathway by miR-146a-SPIONs in cell lines. (A) Preparation of miR-SPIONs. (B) The NF-κB pathway and miR-146a target in aortic macrophage and EC. (C) Representative confocal images showing the ex vivo association of Cy5-labeled PEG-SPIONs and miR-146a-SPIONs (red; with white arrows) to macrophages, ECs and SR-A in atherosclerotic plaques from aortic root sections. Green pseudo color: CD68 (macrophages), ICAM-1 (ECs) or SR-A. The white dotted lines indicate the border of the vascular wall from aortic roots. (D) Flow cytometric analysis shows the association of Cy5-labeled PEG-SPIONs (blue) and miR-146a-SPIONs (red) to total macrophages and total ECs in the aorta of ApoE−/− mice after 2 h of ex vivo incubation (n = 4–6, across two independent experiments). Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's test for post hoc analysis. (E and F) In vitro down-regulation of genes in RAW264.7 macrophages and C166 ECs related to the NF-κB proinflammatory pathway 24 h following incubation of miR-146a-SPIONs (red) or PEG-SPION (blue) (n = 5, across two independent experiments). Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t test. All the data are presented as mean ± SEM.