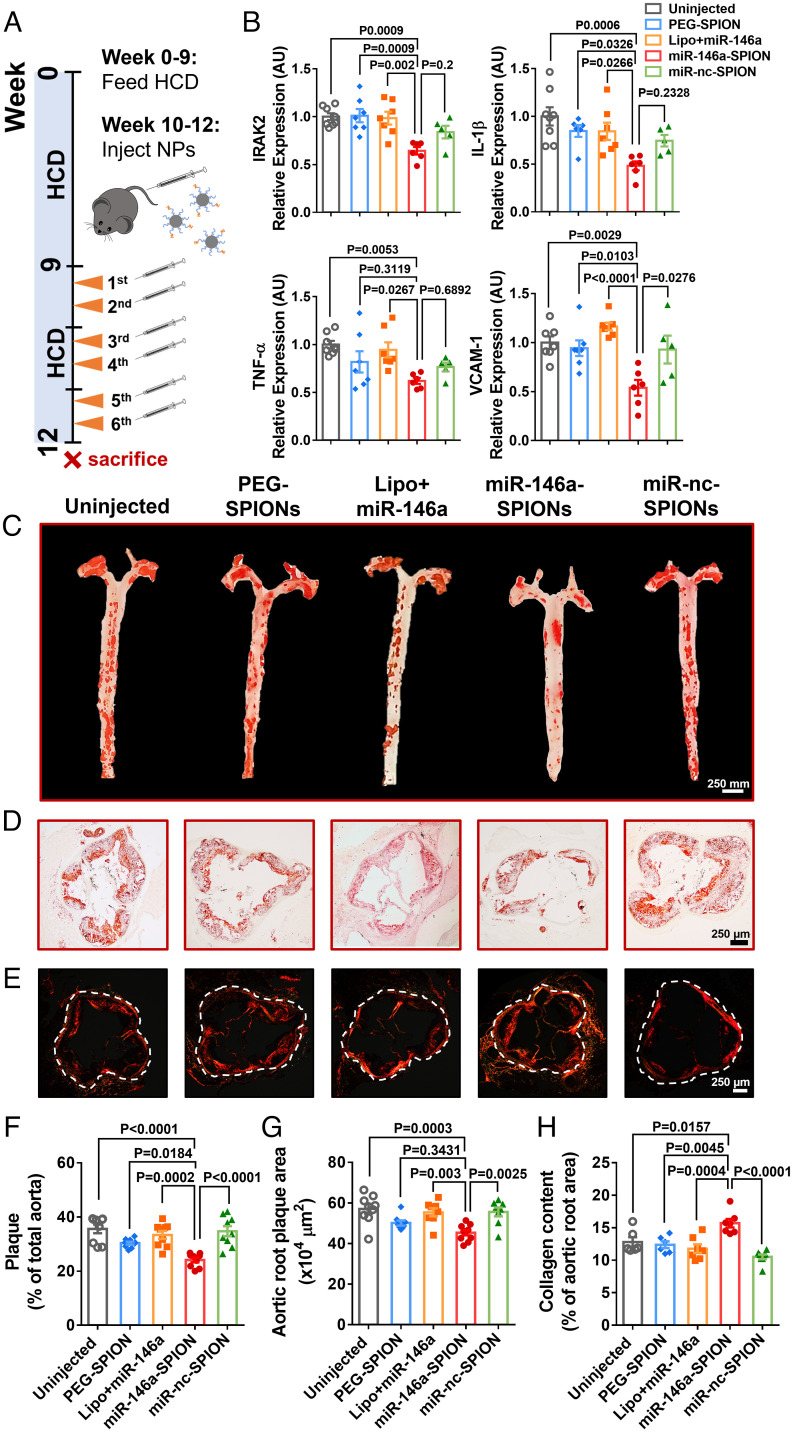
Fig. 3.
miR-146a-SPIONs reduced and stabilized atherosclerotic plaques and inhibited genes linked to atherogenesis. (A) After 9 wk of HCD, the ApoE−/− mice received two weekly i.v. injections from weeks 10–12 while continuing the HCD. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of aortic RNA reveals significant down-regulation of genes targeted by miR-146a (IRAK2) and genes downstream of the NF-κB pathway (IL-1β, TNF-α, and VCAM-1) by miR-146a-SPIONs. For the miR-146a-SPION group, representative images of (C) Oil Red O (ORO)-stained intact aortas and (D) ORO-stained sections of aortic roots indicate most substantial reduction in the plaque fat content (red), and (E) Sirius Red-stained aortic roots reveal most abundant accumulation of collagen (red). For the miR-146a-SPION group, the (F) fractional plaque area in total aorta (n = 8–10 mice per group, across three independent experiments) is the lowest, (G) plaque area in the aortic root is the lowest, and (H) collagen content in aortic root is the highest. Data of aortic root sections were chosen from n = 6 images per mouse from n = 6–8 mice per group. Data are presented as means ± SEM. Statistical significance was calculated by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's test for post hoc analysis.