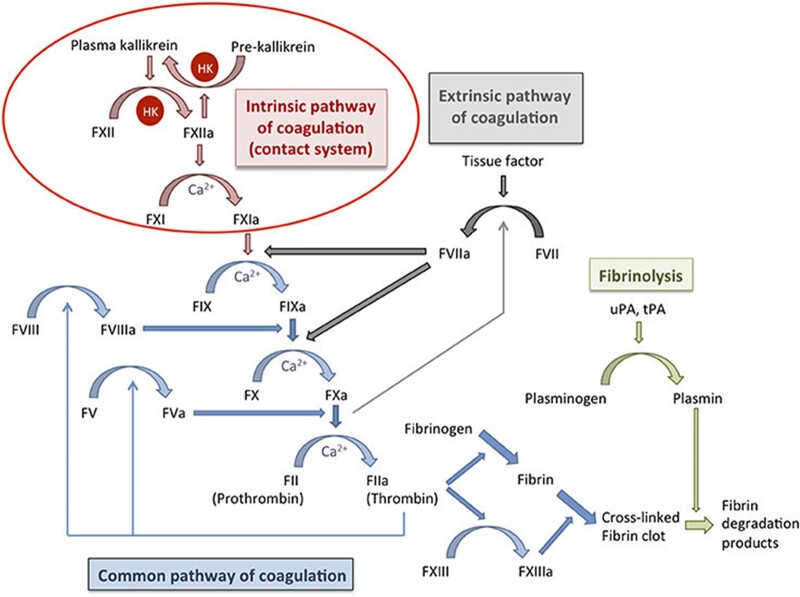
Figure 1.
The schematic representation of the coagulation cascade, which includes the intrinsic pathway, extrinsic pathway and common pathway. Both the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways converge at the common pathway and lead to factor X activation, which helps convert prothrombin to thrombin. Thrombin is necessary to convert fibrinogen to fibrin and activate factor XIII, which eventually leads to a crosslinked fibrin clot. Fibrinolysis helps regulate hemostasis and helps degrade the fibrin network via plasmin. HK, high molecular weight kininogen; uPA, urokinase plasminogen activator; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator. Image adapted with permission from Loof et al. [29].