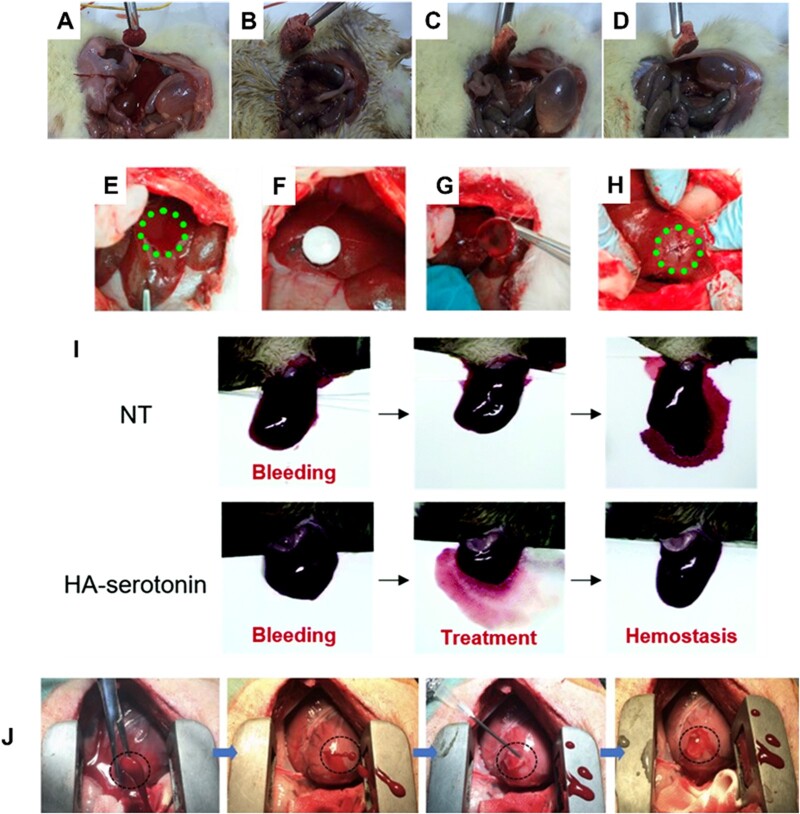
Figure 3.
In vivo hemostasis studies using polysaccharide-based hemostats. (A) Standard gauze, (B) SF-coated bacterial cellulose/chitosan, (C) SF-coated Vit K/bacterial cellulose/chitosan, (D) SF-coated protamine sulfate/bacterial cellulose/chitosan applied to the bleeding site in a diabetic rat femoral artery model. Images adapted with permission from Karahaliloglu et al. [79], (E) creation of liver injury in the exposed left medial lobe of a New Zealand rabbit, (F) treatment of the injury site with aldehyde dextran (PDA) sponges. Hemostasis was maintained after removing the PDA sponge (G) and even after squeezing the wound (H). Images adapted with permission from Liu et al. [84]. (I) Liver hemorrhage model of factor VIII-deficient hemophilia mice with no treatment (NT), and HA-serotonin hemostatic adhesives. Image adapted with permission from An et al. [99]. (J) Six-millimeter cardiac puncture injury in pig hearts followed by treatment with methacrylated HA show rapid hemostasis and sealing following UV-induced polymerization. Image adapted with permission from Hong et al. [101].