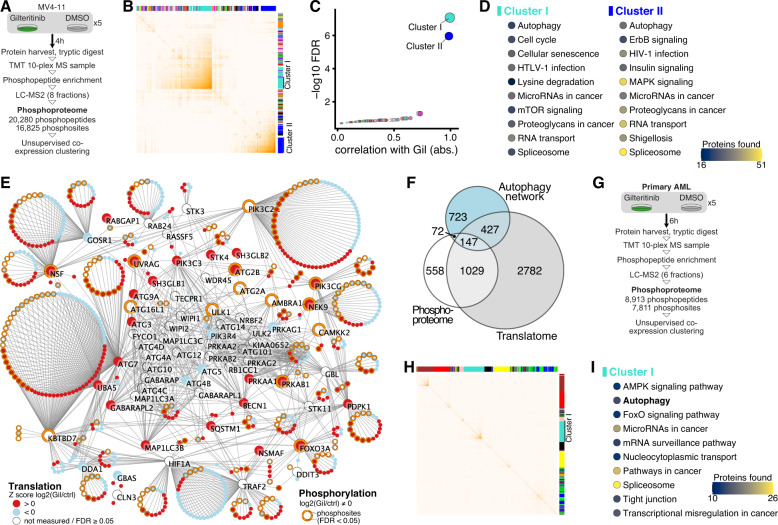
Fig. 2. Integration with phospho-proteomics identifies the autophagy network as the major target of cellular co-regulation following FLT3-ITD inhibition.
A Experimental scheme. MV4-11 cells were treated with 10 nM gilteritinib or DMSO control for 4 h (n = 5). B Heatmap depicting unsupervised co-expression clustering of quantified phosphosites. Individual clusters are identified by distinct colors on top row and right column. C Correlation (absolute) of phosphosite co-expression clusters with experimental treatment condition and associated statistical significance (FDR, false discovery rate). D KEGG pathway analysis on the two clusters identified by unsupervised co-expression clustering which were significantly associated with gilteritinib treatment. The top ten significant (P < 0.05, adjusted for multiple testing by g:SCS) pathway annotations are listed alphabetically for each cluster. E Translatome and phospho-proteome data (gilteritinib, MV4-11) mapped onto the network of human core autophagy proteins and their high-confidence (>0.9) STRING interactors. Core autophagy proteins are labeled. Node fill color shows significant (FDR < 0.05), global Z-scored log2 FC in protein translation. Circle segments around nodes indicate individual, significantly changing phosphosites (FDR < 0.05). F Euler diagram of E, showing the number of proteins with significant changes in translation and phosphorylation upon gilteritinib treatment in MV4-11 cells, mapped onto the autophagy network. G Experimental design. Primary FLT3-ITD + AML cells were treated with 10 nM gilteritinib or DMSO for 6 h (n = 5). H Heatmap depicting unsupervised co-expression clustering of quantified phosphosites. Individual clusters are identified by distinct colors on top row and right column. I KEGG pathway analysis on the main phosphosite cluster identified by unsupervised co-expression clustering. The top ten significant (P < 0.05, adjusted for multiple testing by g:SCS) pathway annotations are listed alphabetically.