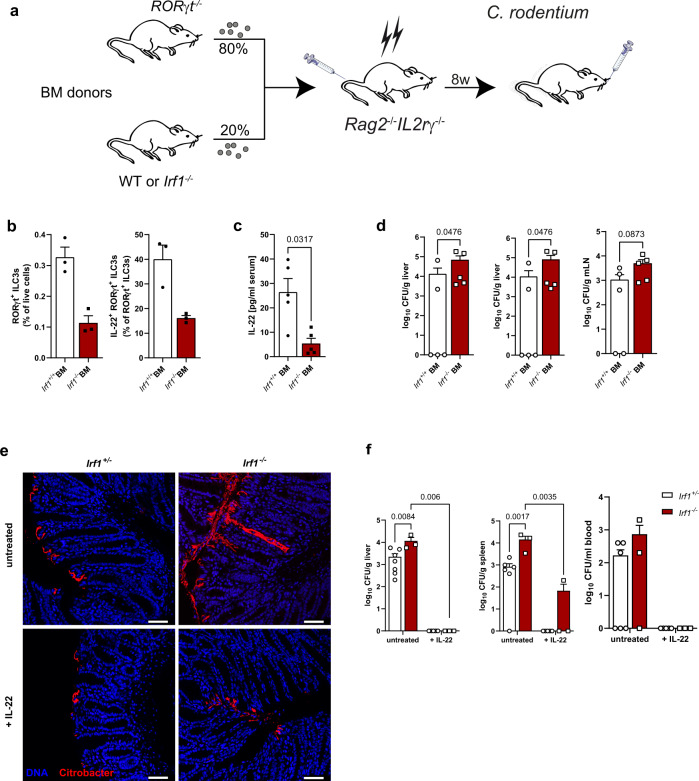
Fig. 8. IL-22 treatment protects Irf1–/– mice from systemic C. rodentium dissemination.
a Mixed bone marrow (BM) chimeras with 80% RORγt–/– (ILC3 deficient) and 20% control or Irf1–/– bone marrow were generated. After 8 weeks, mice were infected with C. rodentium and analyzed at 8 dpi. b Flow cytometric analysis of ILC3s (lin-Thy1.2+RORγt+) and ILC3s expressing IL-22 (n = 3/group). c Serum IL-22 concentrations were measured by specific ELISA (n = 5/group). d Dissemination of C. rodentium was analyzed by determination of CFU/g tissue from livers, spleens and mLNs (n = 5/group). e, f Control and Irf1–/– mice were injected with an Il22 expression vector. After three days, mice were infected with C. rodentium. e C. rodentium colonization of the colonic epithelial surface was visualized by staining of colonic cross sections. Scale bars represent 50 µm. f Dissemination of C. rodentium was analyzed by determination of CFU/g tissue from livers (Irf1+/–: untreated n = 7, IL-22 n = 5; Irf1–/–: n = 3/group), spleens (Irf1+/–: untreated n = 6, IL-22 n = 5; Irf1–/–: n = 3/group) and CFU/ml blood (Irf1+/–: untreated n = 6, IL-22 n = 5; Irf1–/–: n = 3/group). Data is expressed as mean ± SEM. Exact p values defined by two-tailed Mann–Whitney U test (b–d) or 2way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (f) are provided in the plots. Source data are provided as a Source data file.