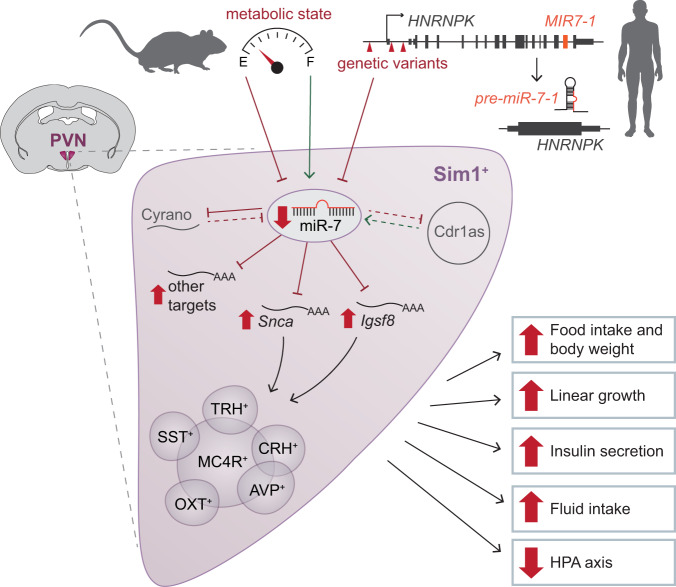
Fig. 7. The role of miR-7 in Sim1 neurons to regulate mammalian energy homeostasis and neuroendocrine function.
In mice, hypothalamic expression of miR-7 is regulated by metabolic state. In humans, variants in the locus encompassing miR-7 are associated with reduced expression of HNRNPK/MIR-7-1. miR-7 regulates the expression of the noncoding RNAs Cyrano and Cdr1as (dashed lines indicate previously published data35). Loss of miR-7 expression in Sim1 neurons leads to upregulation of miR-7 target genes, including Snca and Igsf8, to disrupt the function of multiple Sim1 neuron subpopulations. As a result, the absence of miR-7 causes hyperphagic obesity, increased linear growth, increased insulin secretion, increased fluid intake, and suppressed HPA axis function. Green arrows indicate a positive effect on expression; red blunt-headed lines indicate a negative effect on expression.