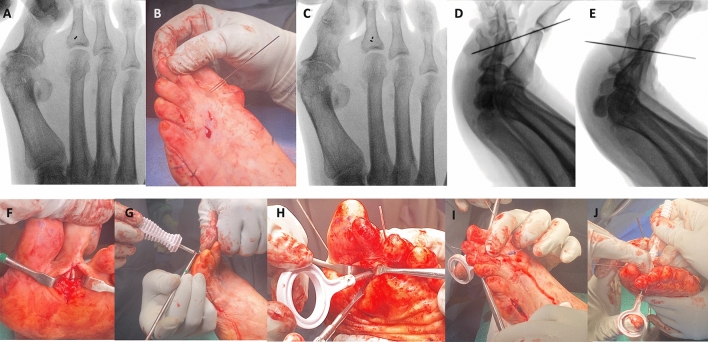
Fig. 1.
Flexor Tenodesis Surgical Technique for the 2nd Toe. a Under fluoroscopic guidance, a K-wire is used to find the level of the base of the proximal phalanx so the dorsal small direct approach can be performed. Ideally, the K-wire should be positioned in the central aspect of metaphyseal area of the proximal phalanx. b-c A second K-wire can be inserted also under fluoroscopic guidance, using the first one as a landmark for ideal positioning. d On the lateral fluoroscopic view, the ideal positioning is so the K-wire should be perpendicular to the plantar aspect of the proximal phalanx. e Since during the first attempt the K-wire was aimed to proximally, it was repositioned and is now more perpendicular to the plantar surface of the proximal phalanx. f Once ideal K-wire positioning is achieved on anteroposterior and lateral fluoroscopic views, the wire is advanced plantarly through the skin, and a plantar longitudinal approach is developed to expose the K-wire, opening the flexor tendon sheath and making sure the wire is positioned in between the two slips of the flexor digitorum longus tendon (FDL). g The manual reamer/drill bit is inserted over the guidewire from plantar to dorsal first, while an assistant retracts the flexor tendons. h The male implant is inserted from plantar to dorsal using the appropriate introducer. Under direct visualization, the spikes of the implant should be grasping both slips of the FDL and Flexor Digitorum Brevis Tendon. i The female component of the implant is inserted from dorsal to plantar through the tip of the introducer. j While keeping the interphalangeal joints in full extension, and the metatarsophalangeal joint in plantarflexion, the female component of the implant is tightened dorsally into the male implant