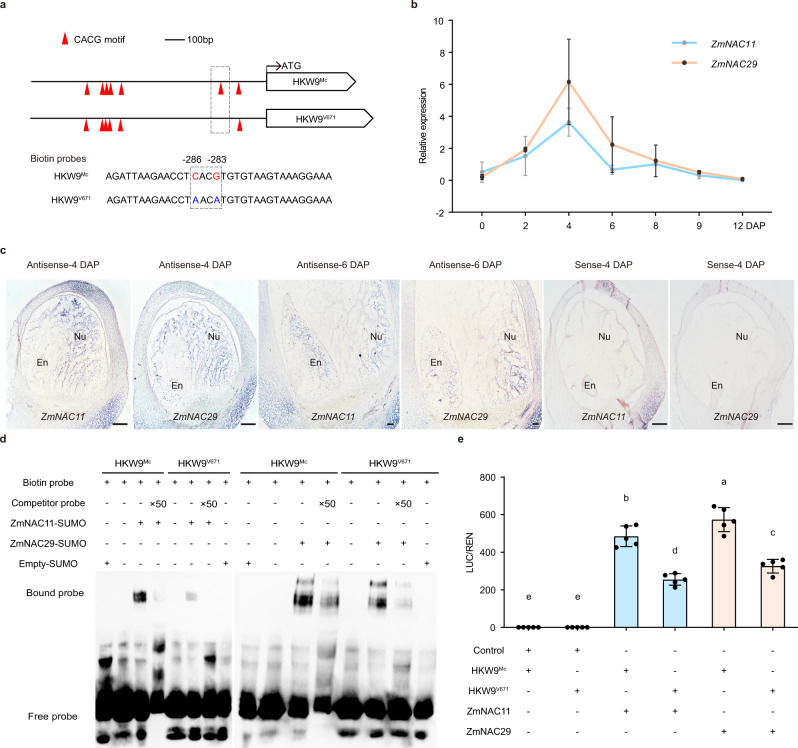
Fig. 5. Nucellus-expressed ZmNAC11 and ZmNAC29 bind to and activate ZmEXPB15.
a Schematic diagrams of the promoters of HKW9Mc and HKW9V671. The red triangles represent in vitro CACG motifs. The dashed box represents the positions of the biotin probes (b), qRT-PCR analysis of ZmNAC11 and ZmNAC29 expression during early kernel development of 0 to 12 DAP. All expression levels from three biological repeats were normalized to Actin. c In situ localization of ZmNAC11 and ZmNAC29 expression in the developing kenrels at 4 and 6 DAP. Positive signals were found in the nucellus (Nu) and endosperm (En) using the ZmNAC11 and ZmNAC29 antisense probes. The control was performed using 4-DAP kernel with ZmNAC11 and ZmNAC29 sense probes. Scale bars = 50 μm. d DNA binding affinities of the recombinant ZmNAC11 and ZmNAC29 proteins on the CACG motif-containing promoter regions of HKW9Mc and HKW9V671 detected by electrophoresis mobility shift assays (EMSAs). ZmNAC11 and ZmNAC29 bind more strongly to the promoter fragment (−299 to −249 upstream of the ATG) from the large-kernel line HKW9Mc than to that from the small-kernel line HKW9V671. The unlabeled intact probes were used for competition. The experiment was repeated two times with a similar result. e Transactivation activities of the ZmNAC11 and ZmNAC29 proteins on ZmEXPB15 promoters of two NILs (HKW9Mc and HKW9V671). Values are means ± s.d. (n = 5 biologically independent samples), Tukey HSD test is used and the statistical differences (P < 0.05, two-sided) are indicated by different letters. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.