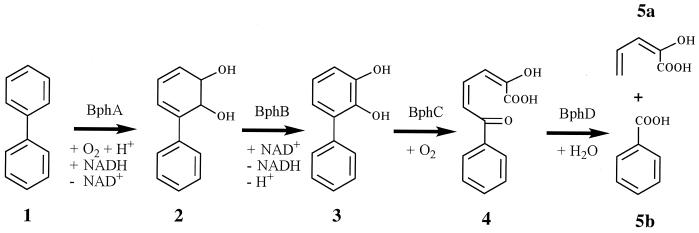
FIG. 1.
Attack on an aromatic compound by a ring-hydroxylating dioxygenase and subsequent catabolic reactions, exemplified by biphenyl (e.g., see references 1, 6, 14, 20, and 25). Enzymes; BphA, biphenyl 2,3-dioxygenase; BphB, biphenyl-2,3-dihydrodiol 2,3-dehydrogenase; BphC, 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl 1,2-dioxygenase; BphD, 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoate hydrolase. Compounds: 1, biphenyl; 2, biphenyl-2,3-dihydrodiol; 3, 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl; 4, 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoic acid; 5a, 2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoic acid; 5b, benzoic acid.