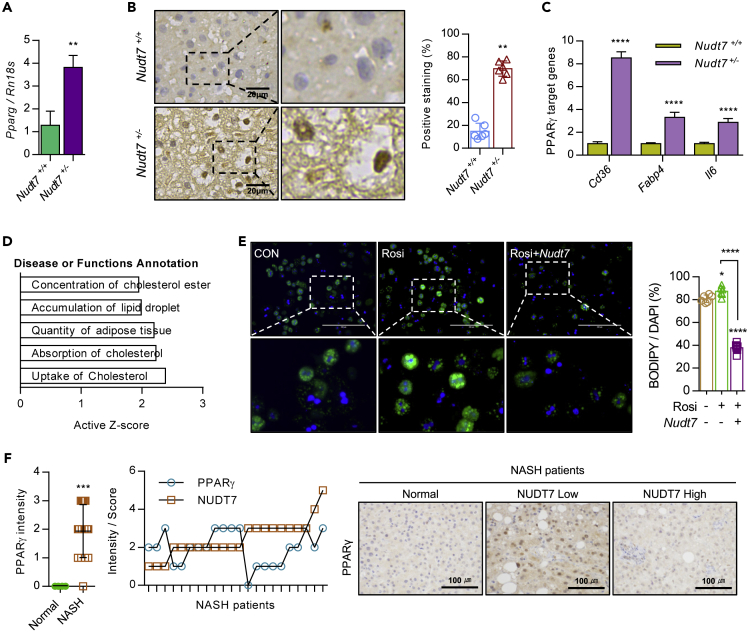
Figure 4.
Activation of PPARγ in Nudt7+/− liver is responsible for hepatic lipid accumulation
(A) The expression level of Pparg in Nudt7+/+ and Nudt7+/− mouse liver was analyzed using qRT-PCR.
(B) Representative image of PPARγ in 12-month-old Nudt7+/− liver compared to Nudt7+/+ liver (n = 3; Scale bars, 20 μm) and positive staining ratio (n = 6 per group).
(C) The expression levels of PPARγ target genes (Cd36, Fabp4, and Il6) were analyzed by qRT-PCR (n = 3).
(D) Genes related to PPARγ signaling were extracted from the RNA sequencing data (n = 3) and subjected to IPA.
(E) Representative images of BODIPY493/508 staining and positive cell counting (n = 6 per group) in primary cultures of Nudt7+/− hepatocytes in the presence of 10 μM rosiglitazone (Rosi) with pcDNA-Nudt7 for 24 h. Scale bars, 200 μm.
(F) Representative images and intensity of PPARγ in NASH liver (n = 22) compared to normal liver (n = 4) biopsy. Scale bars, 100 μm. ∗p ≤ 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (Unpaired t-test or onw-way ANOVA).