Figure 1.
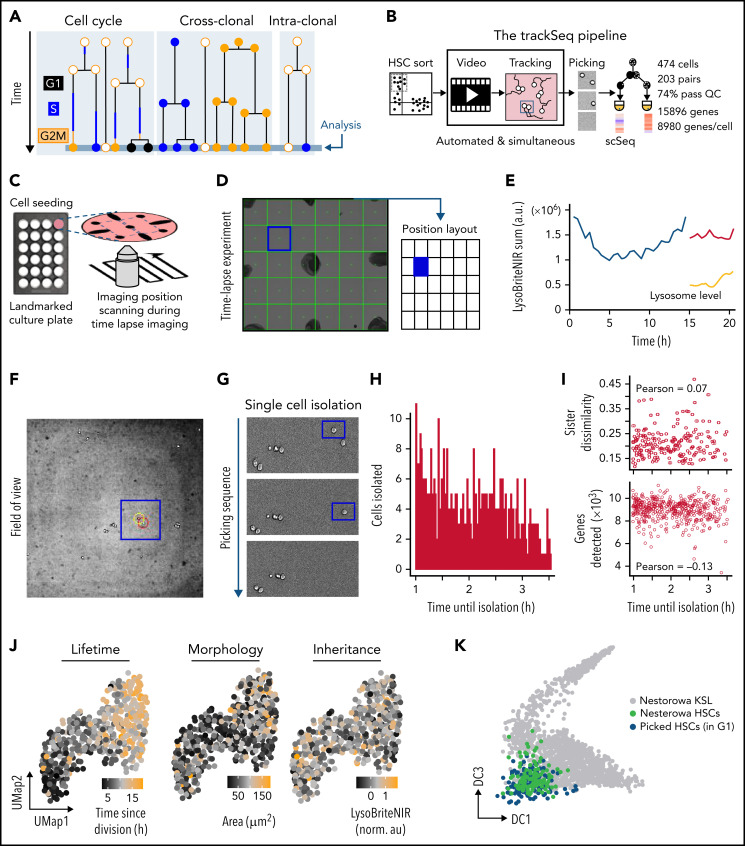
Integrating scRNA-Seq with quantitative time-lapse imaging to identify relevant intra-clonal differences. (A) Transcriptional differences between paired daughter cells (intra-clonal differences) are obscured by CC and cross-clonal differences. (B) trackSeq workflow and performance. Automated real-time event detection in ongoing live cell imaging experiments and convenient cell position navigation by alerT software. Landmarks (eg, manual sharpie dots) mark culture dishes (C) for fast visual co-registration between time lapse and cell picker microscopy field-of-views (D). (E) alerT provides dynamics quantifications from automated cell tracking for quick control by the user. (F) For each identified cell, alerT displays its colony position within the imaging position (field-of-view, panel D). (G) Sequential cell isolation steps are visually logged by alerT. (H-I) Delays in cell picking have no transcriptional effect. (H) Time delays between last observations until picking for each cell used in this study. (I) Used delays do not influence quality of single-cell transcriptional profiles (number of genes detected) or transcriptional sister dissimilarity. (J) Examples of cell properties linked to HSC daughter scRNA-Seq profiles. (K) trackSeq culture and isolation has little impact on HSC transcriptomes. Isolated HSC daughters (blue) in G1 map closely to freshly isolated HSCs (green) in reference landscape of early adult hematopoiesis.24 a.u., arbitrary units; QC, quality control; UMap, Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection.