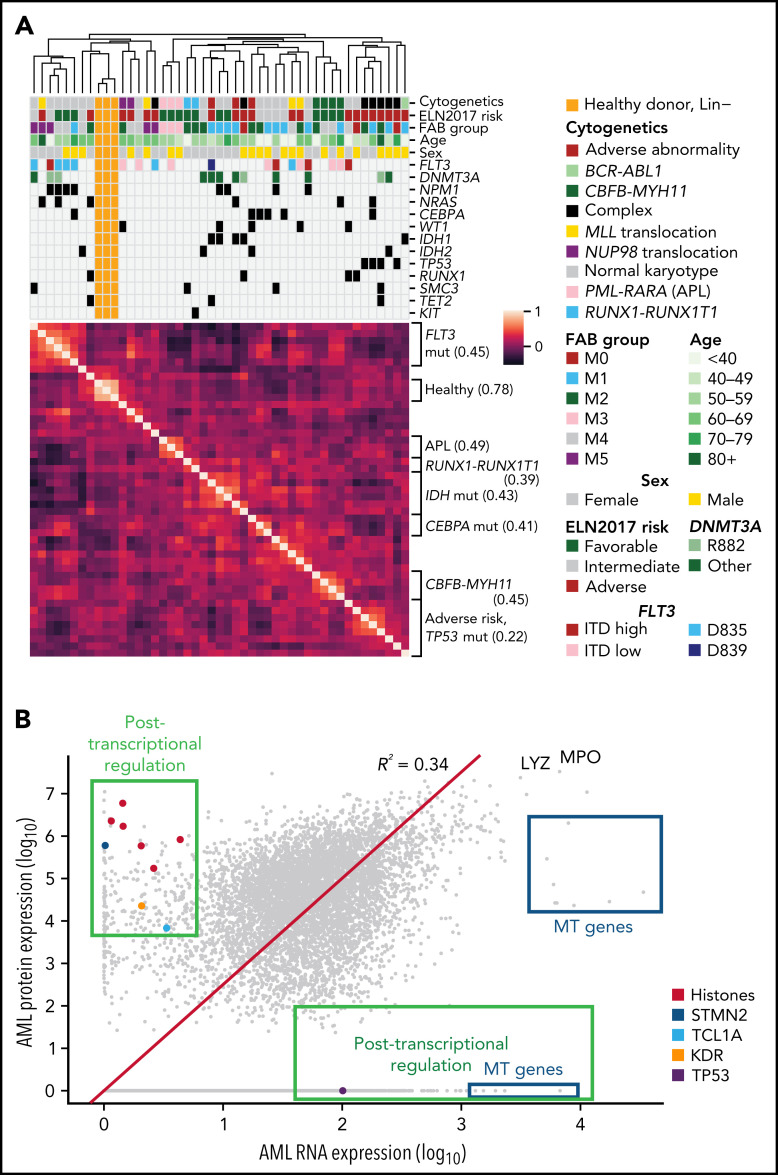
Figure 2.
Protein expression levels are often correlated with clinical features and reveal evidence for posttranscriptional regulation. (A) Unsupervised clustering of proteomic profiles, revealing distinct clusters of samples, many of which correlate with known molecular covariates, including cytogenetic alterations, FAB subgroups, and recurrent mutations. The heatmap shows a Pearson correlation of protein expression levels among all patients using TMT proteomic measurements. Clustering was based on the unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean algorithm, with similarity scores as shown in the heatmap. Brackets on the side of the heatmap indicate subgroups with shared clinical or molecular features; the value in parentheses indicates the mean Pearson correlation among members of that subgroup. (B) Mean log10 expression values of protein and RNA abundance for 7916 proteins measured in the bone marrow samples of 44 de novo, primary AML patients at time of diagnosis. RNA expression was quantified using transcripts per million from RNA sequencing after log10 transformation. Protein expression was measured using LFQ tandem mass spectrometry with normalized precursor ion intensities representing protein abundance after log10 transformation. The red line shows a line of best fit using linear regression with no intercept. Proteins displaying evidence for posttranscriptional regulation (high protein expression with low RNA expression or vice versa) are boxed in green and include the labeled histones H1-3, H1-4, H1-5, H2AC21, H3C1, and H3C15, as well as STMN2, the AKT co-activator/oncogene TCL1A, the protein tyrosine kinase receptor KDR, and the key tumor suppressor TP53. High protein, low RNA green box includes proteins with at least half of the maximal protein expression detected (log10 scale) and at most 15% of the maximal RNA expression. High RNA, low protein green box includes proteins with <25% of the maximal protein expression and at least median RNA expression. All proteins in the blue boxes are mitochondrially (MT) encoded and have lower-than-expected protein expression values as predicted by RNA expression. LYZ and MPO are known highly abundant proteins in myeloid cells. mut, mutant.