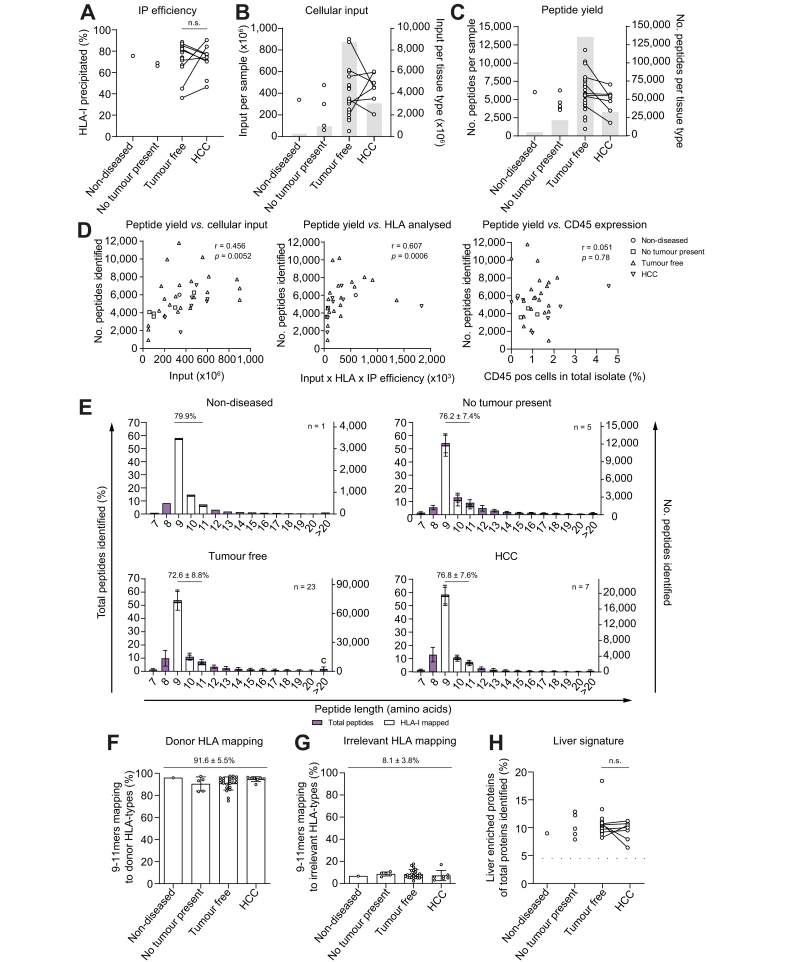
Fig. 2.
HLA-I immunoprecipitation monitoring.
(A) IP efficiency by western blot. ns: non-significant by the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. (B) Hepatocyte input for IP per sample (individual data points; left y-axis) and cumulative across tissue types (grey bar diagrams; right y-axis). (C) Number of peptides identified per sample (individual data points; left y-axis) and cumulative across tissue types (grey bar diagrams; right y-axis). (D) Correlation of peptide yield with cellular input (left; Pearson correlation), cellular input corrected for HLA expression and IP efficiency (middle; Spearman correlation), or presence of CD45-expressing cells in the hepatocyte isolate (right; Spearman correlation). (E) The length distribution of identified peptides as percentage of total peptides identified (left y-axis) and as absolute number (right y-axis). The average percentage of 9–11mers ± SD is displayed above the graphs. 9–11mers mapping to donor HLA with a rank score ≤2.0% (NetMHCpan4.1) are distinguished in white. Error bars represent the SD. Percentage of 9–11mers (F) mapping to at least 1 donor HLA type or (G) mapping to HLA types for which the corresponding donor is negative. F and G: indicated is the overall mean ± SD. (H) Representation of liver-enriched proteins per tissue type as percentage of total source proteins presented in HLA-I. The percentage of liver-enriched proteins in the human genome (n = 936 out of 20,999) was 4.5% (dotted line). n.s.: non-significant by the Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed-rank test. HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; HLA, human leucocyte antigen; HLA-I, human leucocyte antigen class I; IP, immunoprecipitation.