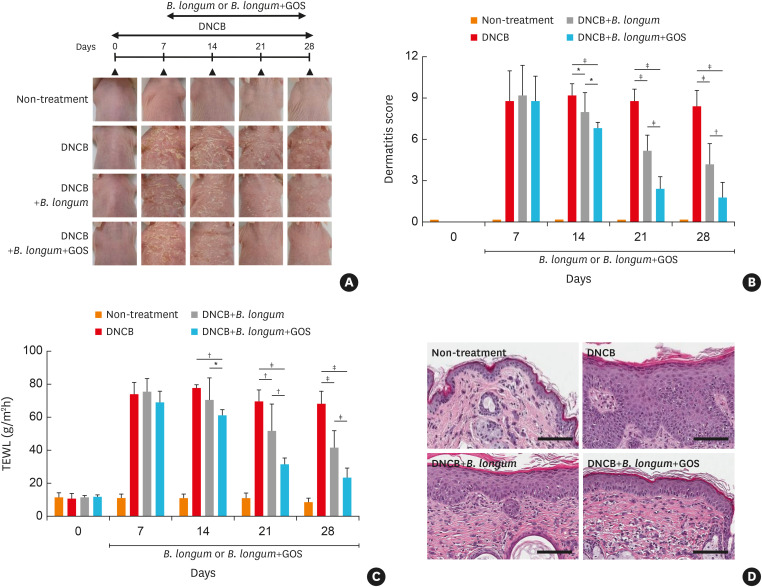
Fig. 2. The effects of B. longum or synbiotic mixtures of B. longum and GOS on DNCB-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin and skin barrier dysfunction in a murine model. Hairless mice were treated with DNCB for the initial 7 days and continually treated with DNCB alone, DNCB with B. longum or DNCB with synbiotics (B. longum with GOS) for additional 21 days. Experimental design and features of mouse skin are shown (A). Dermatitis scores (B), TEWL (C), and H&E staining (original magnification, ×800) (D) were evaluated. The data are shown as the mean ± SEM of 2 independent experiments (n = 5 mice per group; scale bar = 100 μm).
B. longum, Bifidobacterium longum; GOS, galactooligosaccharide; DNCB, dinitrochlorobenzene; TEWL, transepidermal water loss.
*P < 0.05, †P < 0.01, ‡P < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with the Tukey-Kramer test.