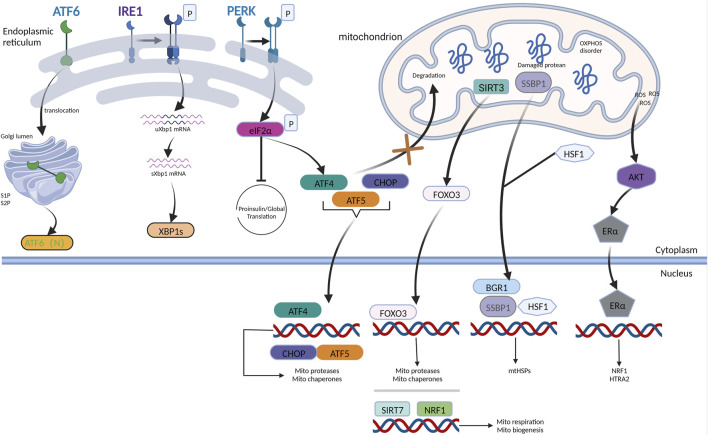
FIGURE 1.
UPRmt mechanism in mammals. The AKT-ER axis is induced by the accumulation of ROS in IMS to trigger the transcription of NRF1 and HTRA2 upon responding to IMS damage. When ATF5 receives the signal derived from the dysfunctional mitochondria, it influxes into the nucleus, accompanied by ATF4 and CHOP, facilitating the production of chaperones and proteases belonging to mitochondria. HSF1 combines with SSBP1, forming a complex bound to the chromatin remodeling protein BRG1, prompting the expression of mtHSPs. Mitophagy and oxidative stress can trigger the transduction of SIRT3-FOXO3 signaling pathways. NRF1 coordinating with SIRT7 reduces the burden of damaged proteins via inhibition of mitochondrial respiration and synthesis. In conclusion, the mammalian UPRmt facilitates mitochondrial recovery and maintains proteostasis via multiple mechanisms. IRE1, PERK, and ATF6 are three ER stress sensors that monitor protein-folding conditions in the ER lumen. PERK-ATF4 axis is the main hub coordinating UPRER and UPRmt.