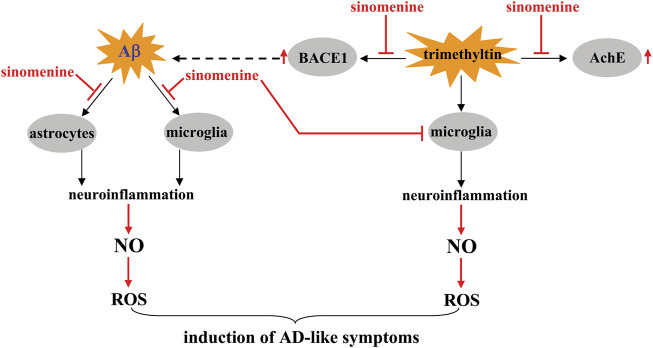
FIGURE 3.
Effects and mechanisms of sinomenine in pathological conditions similar to AD. Sinomenine can suppress Aβ-triggered neuroinflammation mediated by microglia and astrocytes, thereby reducing the accumulation of NO, which in turn reduces the production of ROS Shukla and Sharma (2011), Singh et al. (2020). Under trimethyltin-stimulated conditions, sinomenine suppresses the progression of neuroinflammation mediated by microglia, thereby also reducing the accumulation of NO and ROS Rostami et al. (2022). Meanwhile, sinomenine was found to suppress the trimethyltin-induced overexpression of AchE and BACE1 in brain tissue and reduce the accumulation of a pathological trait protein Aβ in the brain through the latter effect Rostami et al. (2022).