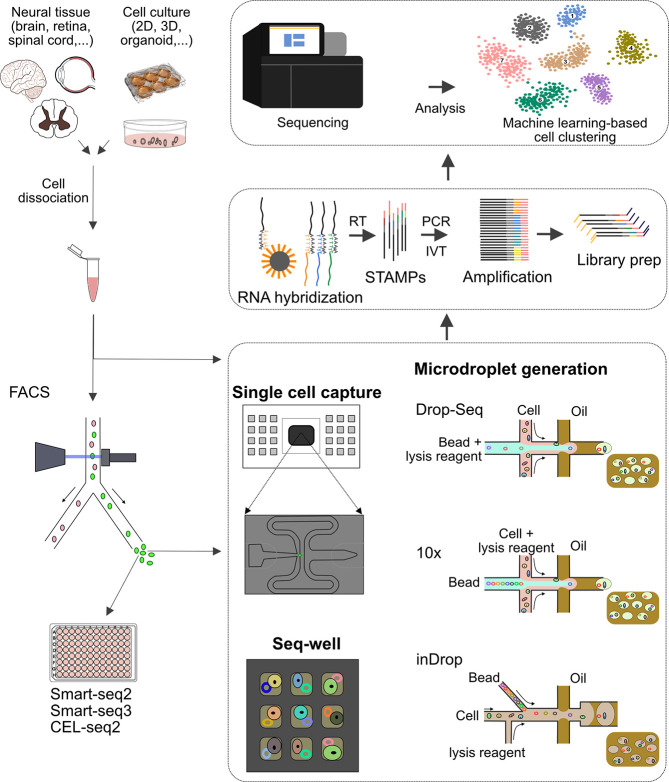
Figure 3.
Contribution of microfluidics-based concepts to scRNA sequencing. Cells obtained either from primary neuronal tissues or from models engineered in vitro are dissociated and sorted by FACS. Purified cells are processed using either low-throughput RNA-Sequencing tools like Smart-Seq and CEL-Seq, or high-throughput microfluidic systems. In general, three main microfluidic approaches are used for single-cell analysis: valve-based (e.g., Fluidigm 1), droplet-based (Drop-Seq, inDrop, 10× Chromium, and Quartz-Seq), and microwell-based (Seq-well) systems. In all cases, trapped single cells are lysed, their RNA is hybridized and reverse transcribed (RT), and cDNA is then amplified either by PCR or linear isothermal amplification by T7-based in vitro transcription (IVT). Thereafter, the cDNA libraries generated in these steps are sequenced, and the data are demultiplexed, aligned to a reference transcriptome, and interpreted for classification of neuronal cell subpopulations. STAMP: single-cell transcriptomes attached to microparticles.