Figure 25.
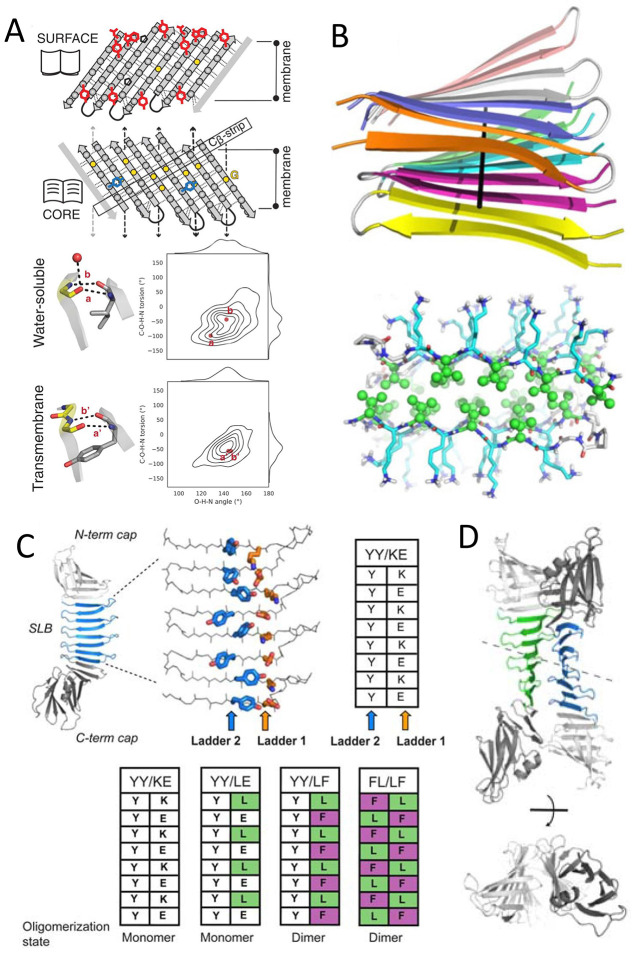
(A) Top: sequence features defining de novo transmembrane β-barrel fold and shape. Hydrogen bonds (dashed lines) connect β-strands in the designs. Side chains are shown as gray spheres and G residues as yellow dots. Aromatic girdle motifs are shown in red, Y residues of the mortise-tenon motifs in blue, and P residues as black pentagons. Glycine kinks bend the β-sheets into four corners (arrows). Bottom: hydrogen bond geometries between pairs of residues involving a glycine kink, comparing crystal structures of water-soluble (PDB ID: 6CZH) and transmembrane β-barrels (PDB ID: 1BXW). Glycine residues are in yellow. Water molecules are shown as red dots. Distributions of the C–O–H–N and O–H–N angles are shown to describe the corresponding hydrogen bond geometry. Reprinted with permission from ref (175). Copyright 2021 The American Association for the Advancement of Science. (B) Structures of the amyloid fibril MAX1 showing: strands align perpendicular to the main fibril axis (top, PDB ID: 2N1E), and residue arrangements (bottom) with K (blue sticks) on the wet interface and V (green ball and sticks) on the dry interface. Reprinted with permission from ref (25). Copyright 2020 Cambridge University Press. (C) Schematic of architecture for PSAMs (PDB ID: 3EC5, 2OY7, 2OY8, 2OYB) with the SLB colored blue and the N- and C-terminal domains colored gray. The side chains of the two cross-strand ladders used as hosts are shown as stick models. The table summarizes the sequences of the ladders in PSAMs. (D) X-ray crystal structures of cross-β PSAMs. The overall structure of the YY/LF PSAM dimer is shown in cartoon representations, in two orthogonal views. The two molecules are related by a pseudo 2-fold symmetry (dashed line). C, D: Reprinted with permission from ref (172). Copyright 2010 National Academy of Sciences.