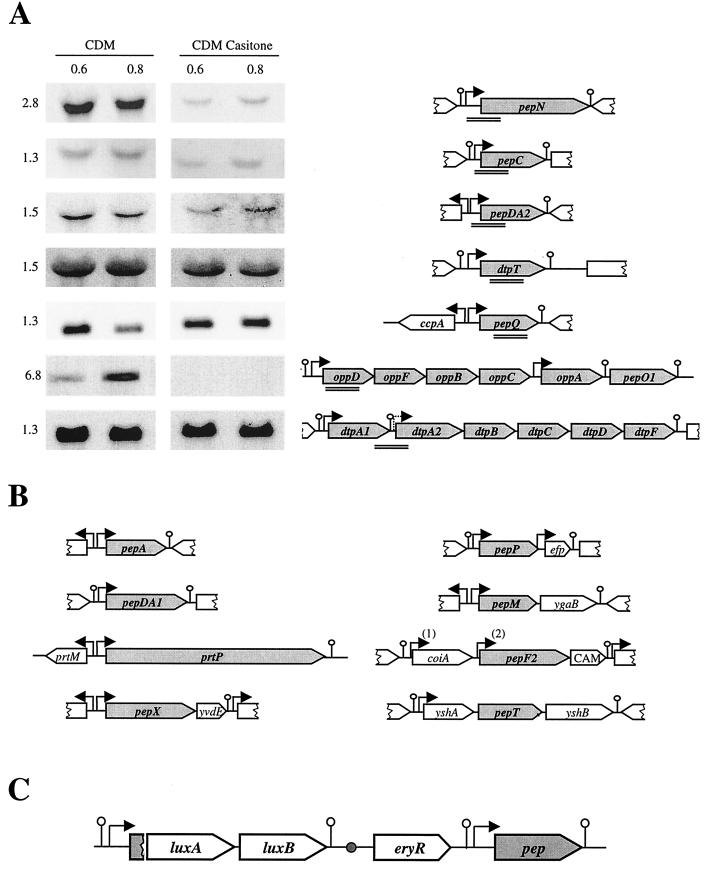
FIG. 2.
Genetic organization of genes encoding the proteolytic system of L. lactis. Schematic representation of the genetic organization of genes was deduced from published papers and completed by data of the L. lactis IL1403 genome sequence (AE005176) as mentioned in the text. (A) Northern blot analysis of the pepN, pepC, pepDA2, pepQ, and dtpT genes and the opp-pepOI and dtpP operons. Total RNA was extracted from L. lactis MG1363 at an OD600 of 0.6 and 0.8 in CDM and CDM Casitone. Total RNA was hybridized with PCR fragments used as probes denoted by double lines. The size of the messenger in kilobases is indicated on the left. Arrows and lollipops present the putative promoters and terminators, respectively. (B) Schematic representation of the genetic organization of prtP, pepA, pepDA1, pepM, pepX, pepP, pepF2, and pepT. Promoters were deduced only from DNA sequence analysis, except for the prtP promoter. The two pepF2 promoters, PpepF21 and PpepF22, are designated by “(1)” and “(2)”, respectively. prtM, efp, and cam (CAM on the diagram) encode the proteinase maturase, elongation factor P, and a potential methyltransferase, respectively. coiA is the counterpart of a gene whose product is involved in competence development in Streptococcus pneumoniae. ygaB, yshA, and yshB encode proteins sharing homology with membrane proteins and transporters, and yvdE encodes a protein similar to proteins of unknown function. Terminators localized downstream of yvdE, efp, and yshB and upstream of yshA and putative promoters localized upstream efp and yshA were deduced, in this work, from the sequence of the IL1403 genome (AE005176). (C) General scheme of the luciferase fusion integrated on the chromosome by single crossover. Upon insertion, the promoter is duplicated and drives expression of the luxAB genes and of the functional gene denoted in grey. The small circle represents the origin of replication of the integrative plasmid that is inactive after the helper plasmid is removed.