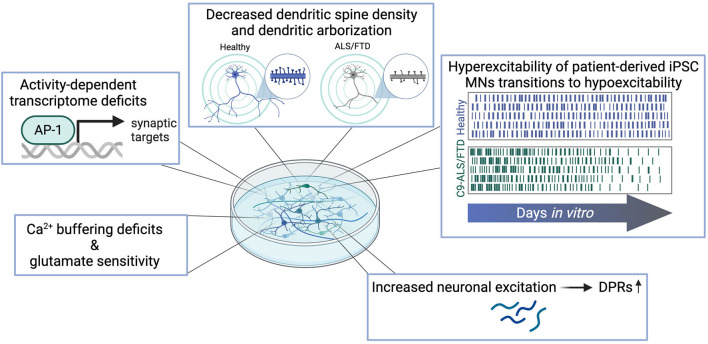
Figure 2.
Synaptic dysfunctions observed in patient-derived in vitro models of C9-ALS/FTD include Ca2+-buffering deficits and increased vulnerability to glutamatergic insult, deficits in the activity-dependent transcriptome, decreased complexity of dendritic arborization and loss of dendritic spines, temporal phases of excitability alterations, and increased DPR levels as a result of hyperexcitation.