Figure 6. ND-Tam produces analgesia in mice with knee hyperalgesia 4 weeks post DMM surgery.
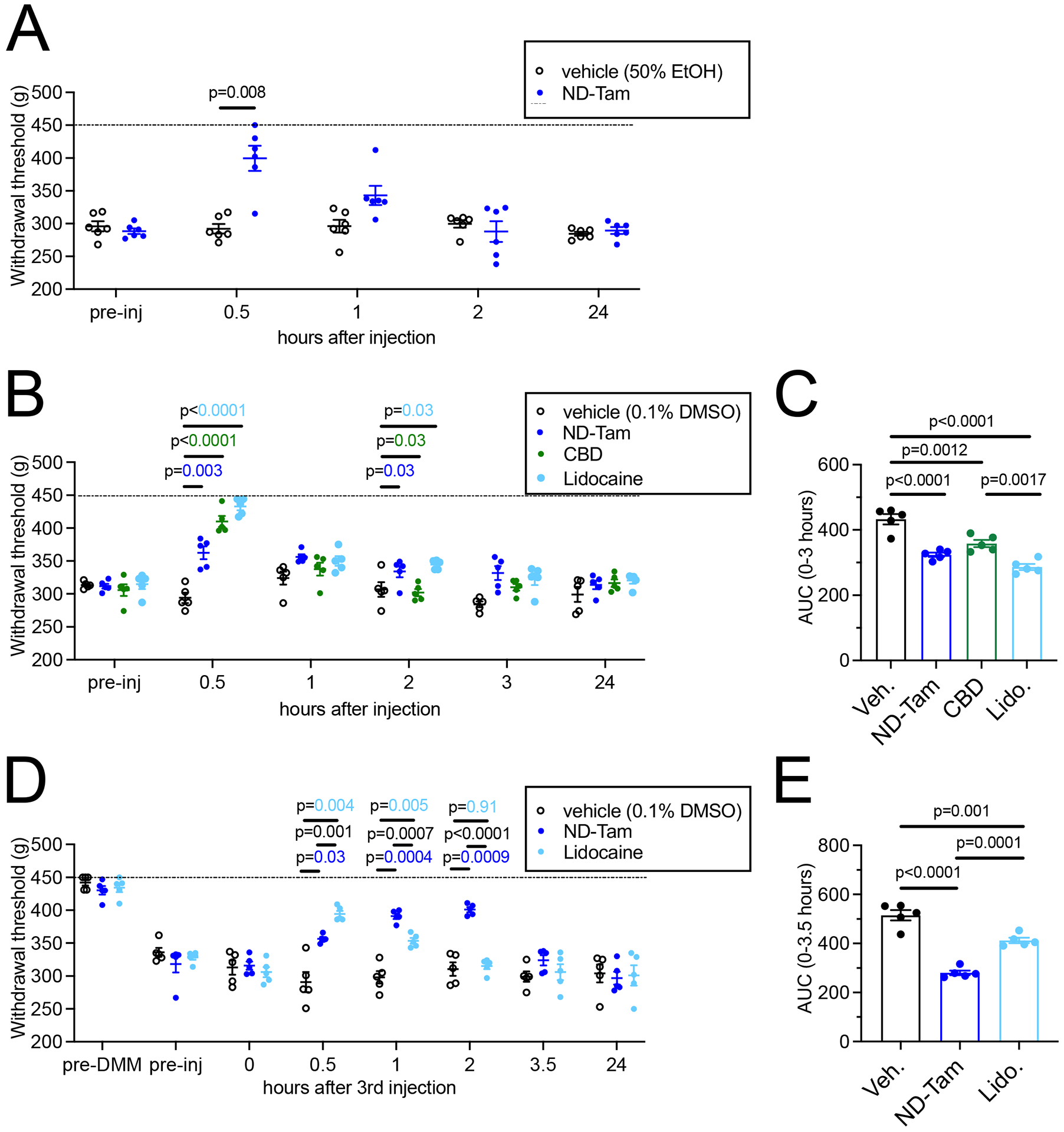
A) Knee withdrawal threshold was measured 4 weeks post DMM surgery and before intra-articular injection of vehicle (50% EtOH) or 50 μM ND-Tam and then at 30 min, 1h, 2h, and 24h post-injection. ND-Tam provided relief from hyperalgesia compared to vehicle 30 minutes after injection (n = 6, P = 0.008). B) Knee withdrawal thresholds assessed 4 weeks post DMM surgery, before and after intra-articular injection of vehicle (0.1% DMSO), 50 μM ND-Tam, 50 μM CBD, or 50 μM lidocaine at 30 min, 1h, 2h, 3h, and 24h time points. P-values are indicated on the graph for time points at which all three drugs are significantly different from vehicle. C) Area under the curve analysis of withdrawal thresholds for vehicle, ND-Tam, CBD, and Lidocaine from 0–3 hours after injection. ND-Tam performed similar to CBD and lidocaine over time (n = 5, P = 0.17, P = 0.13, respectively). D) Knee withdrawal thresholds assessed before DMM surgery (pre-DMM), and 4 weeks post DMM surgery, before (pre-inj) and after 3 days of intra-articular injection of vehicle (0.1% DMSO), 0.5 μM ND-Tam, or 0.5 μM Lidocaine at 0 (day 3 before final injection), 30 min, 1h, 2h, 3.5h, and 24h time points (on day 3 after the final injection). E) Area under the curve analysis of withdrawal thresholds for vehicle, ND-Tam, and Lidocaine from 0–3.5 hours after the 3rd injection. ND-Tam outperforms lidocaine after 3 days of repeated intra-articular injections (n = 5, P = 0.0001). A, B, D) Statistical analysis is stated in the associated data table, Supplemental Table 4; Dashed line indicates maximum of the assay = 450 g.
