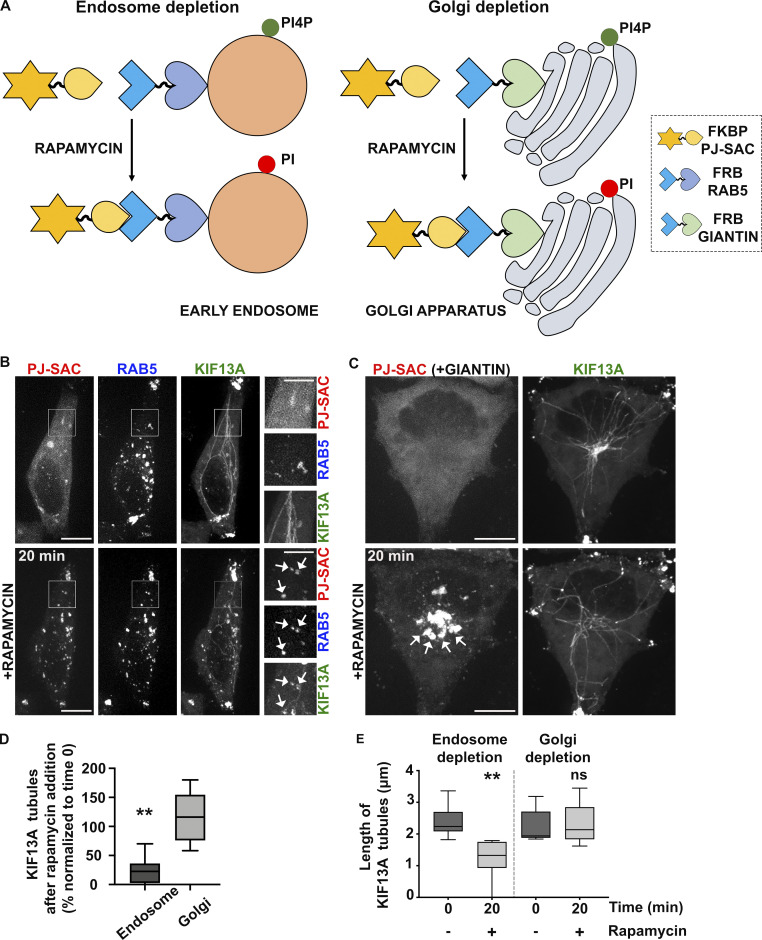
Figure 4.
Depletion of endosomal PI4P destabilizes recycling endosomal tubules. (A) Schematic of the rapamycin-induced FRB-FKBP system allowing the organelle-specific depletion of PI4P through the recruitment of PI4P phosphatase Sac domain (mRFP-FKBP-PJ-SAC) to membranes positive for RAB5 (iRFP-FRB-RAB5, early sorting endosomes; left) or Giantin (FRB-Giantin, Golgi apparatus; right). The recruited Sac domain catalyzes the removal of phosphate from PI4P (green ball) to generate PI (red ball). (B and C) Live imaging frames of HeLa cells co-expressing KIF13A-YFP together with (B) mRFP-FKBP-PJ-Sac and either iRFP-FRB-RAB5 or (C) FRB-Giantin before (top) or after (bottom) 20 min addition of rapamycin (1 μM) to recruit PJ-SAC to either RAB5+ endosomal (B) or Giantin+ Golgi (C) membranes (arrows). Note that acute targeting of PJ-SAC to RAB5+ membranes (B), but not to Giantin+ membranes (C), destabilizes KIF13-YFP+ RE tubules. The FRB-Giantin chimera is not fluorescently tagged, and thus not imaged. (D) Quantification of the average percentage of KIF13A-YFP+ RE tubules remaining 20 min after rapamycin addition relative to time 0 min in cells treated as in B and C (right panels). (E) Quantification of the average length (μm) of KIF13-YFP+ RE tubule before (0 min) and 20 min after rapamycin addition in cells treated as in B and C (right panels). Data presented as box-plots represent at least five independent experiments. ns, non-significant. **, P < 0.01. (D and E): two-tailed unpaired t test; endosome depletion, n = 85 tubules; Golgi depletion, n = 118 tubules. Scale bars: (main panels) 10 μm; (insets) 2.5 μm.