Table 3: Temporary mechanical circulatory support devices.
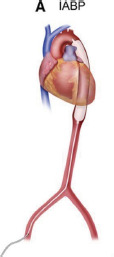
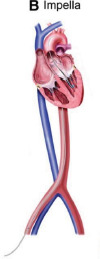
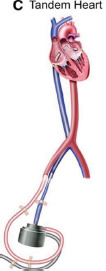
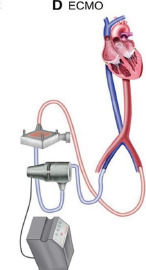
| MCS Device | IABP | Impella 2.5/CP/5.5 | TandemHeart | VA-ECMO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
| CO (L/min) | 0.5–1.0 | 2.5/3.0–4.0/5.0 | 4.0–5.0 | 4.0–10.0 |
| Haemodynamic effects | LV pressure or volume unloading | LV pressure or volume unloading | LV volume unloading | Biventricular pressure and volume unloading |
| Peripheral resistance | Decreased | Decreased | Mildly increased | Highly increased |
| LV unloading | + | ++ | ++ | – |
| Pump mechanism | Pneumatic | Axial flow | Centrifugal | Centrifugal |
| Cannula size | 7–9 Fr | 13–22 Fr | Drainage 21 Fr; Return 15–17 Fr |
Drainage 18–21 Fr; Return 15–22 Fr |
| Advantages | Bedside insertion; no anticoagulation | Direct ventricular unloading | Addition of pulmonary support | Addition of pulmonary support |
| Disadvantages | Minimal haemodynamic support | Mandatory anticoagulation; haemolysis | Immobilization | Incomplete LV unloading |
| Complications | Limb/spinal cord ischaemia; bleeding; aortic dissection | Limb ischaemia; bleeding; haemolysis; ventricular arrhythmias | Cardiac perforation; tamponade bleeding; air embolism; residual ASD | Limb ischaemia; bleeding; stroke; air embolism; circuit clots; DIC; oxygenator failure; altered drug pharmacokinetics |
| Contraindications | Severe PAD; AAA; significant AI | LV thrombus; mechanical AV; severe PAD | VSD; significant AI; left atrial thrombus | Severe PAD; significant AI; aortic dissection |
AAA = abdominal aortic aneurysm; AI = aortic insufficiency; ASD = atrial septal defect; AV = aortic valve; CO = cardiac output; DIC = disseminated intravascular coagulation; ECMO = extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; IABP = intra-aortic balloon pump; LV = left ventricle; PAD = peripheral arterial disease; VA = venoarterial; VSD = ventricular septal defect.
