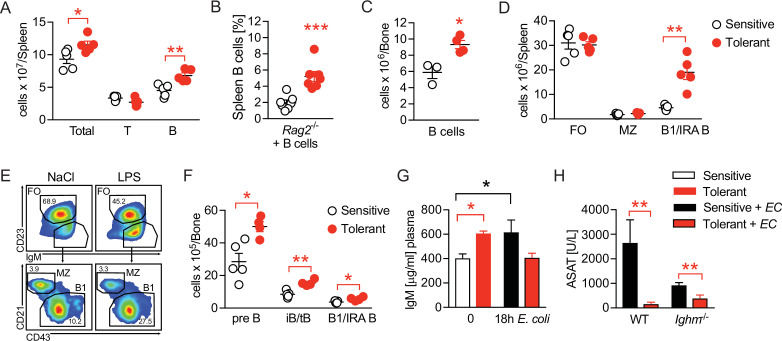
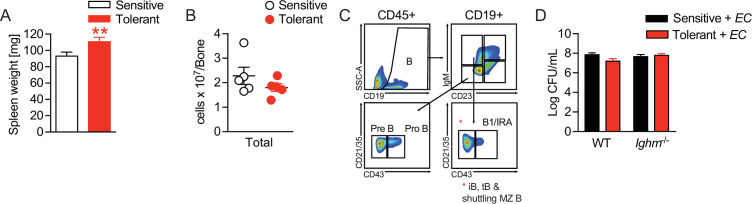
Figure 3. Disease tolerance is associated with rearranged B cell compartments.
(A) Flow-cytometric analysis of B and T cells in the spleen of mice treated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or NaCl 2 weeks earlier. (B) Flow-cytometric analysis of B cells in spleens of Rag2-/- mice treated with LPS or NaCl 2 weeks earlier, and reconstituted with GFP+ B cells before LPS/NaCl. (C) CD19+ B cells per femur of mice treated with NaCl or LPS 2 weeks earlier. (D) Flow-cytometric analysis of FO, MZ and B1/IRA B cells in spleens of mice treated with LPS or NaCl 2 weeks earlier. (E) Gating strategy for splenic B cell subsets. (F) Flow-cytometric analysis of Pre-B, iB/tB and B1/IRA B cells in the bone marrow of mice treated with LPS or NaCl 2 weeks earlier. (G) IgM plasma levels in NaCl or LPS pretreated uninfected mice and 18 hr p.i. with E. coli. (H) Aspartate aminotransferase (ASAT) plasma levels of NaCl or LPS pretreated WT and Ighm-/- mice 18 hr p.i. with E. coli. Data in (A) and (C–F) and are representative out of 2–3 experiments (n=3–8/experimental group). Data in (G–H) are pooled from two independent experiments (n=3–7/experimental group). Data in (B) are from a single experiment (n=7/group) and all data are and presented as mean +/-SEM. * p≤0.05 and ** p≤0.01.