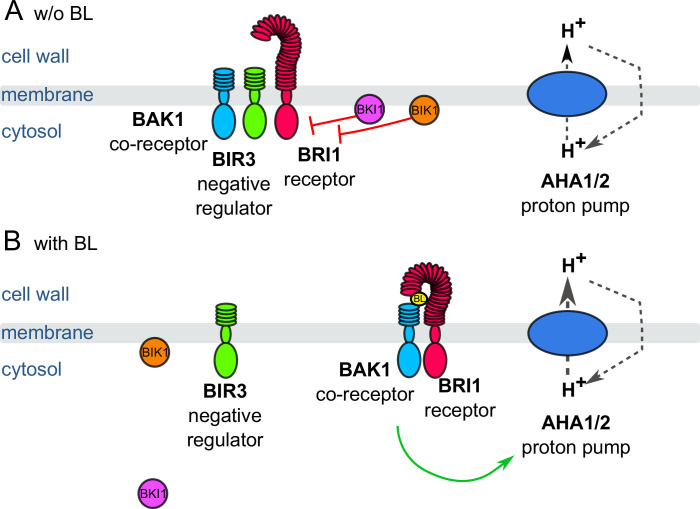
Figure 1. Schematic overview of the key constituents and processes of the plasma membrane-associated fast BR response pathway initiating early steps in cell elongation, here represented by brassinolide (BL).
(A) Inactive state: Co-localizing in a preformed nano-orgnaized complex, the inhibitors BKI1, BIK1 and BIR3 suppresses the activity of BRI1 in the absence of BL keeping the activity of H+-ATPases AHA1 and 2 at basic levels. By interaction with BAK1, BIR3 blocks the access of the co-receptor to BRI1. (B) Active state: Upon BL-binding to the receptor, the inhibitory mechanisms of BKI1, BIK1 and BIR3 on BRI1 and BAK1 are released causing the formation of the active BRI1/BAK1 complex. The complex enhances the AHA activity resulting in cell wall acidification, plasma membrane hyperpolarization and eventually onset of cell elongation. These key constituents and qualitatively described processes were used for the initial establishment of the computational model at cellular.