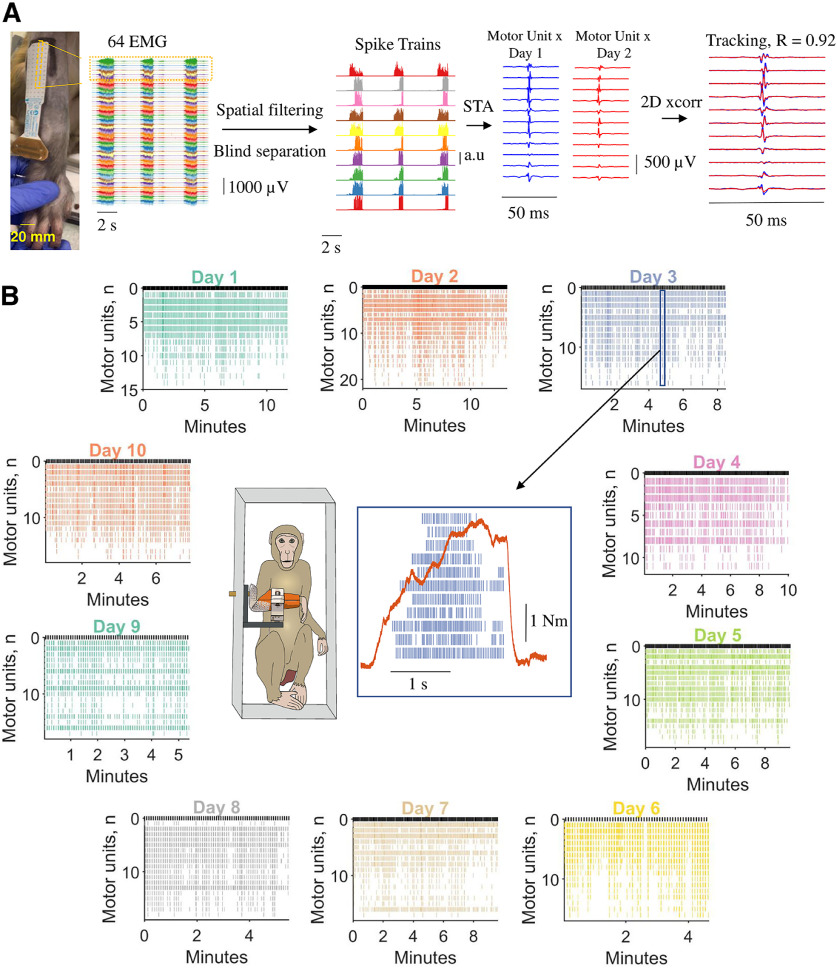
Figure 1.
Motor unit decomposition in awake behaving macaques, experimental framework, and analysis. A, From left to right, 64 monopolar EMG signals during three individual contractions. Each contraction lasted ∼2 s. The monopolar EMG signals were spatially filtered with a double-differential derivation. After this process, blind source separation identified the spike trains belonging to individual motor units. The spike trains for each motor unit were used to spike trigger the average 2D motor unit waveform. The 2D motor unit waveforms were used for the longitudinal tracking, through a 2D cross-correlation function. B, Monkey 1 (MI) individual motoneuron spike trains across the 10 d (color coded). Note that during the different days, we identified a relatively similar number of motor units. The center of the figure shows the experimental setup and an individual voluntary contraction (force signal in red) extracted from day 3. STA, Spike-triggered average. R represents the two-dimensional cross-correlation value.