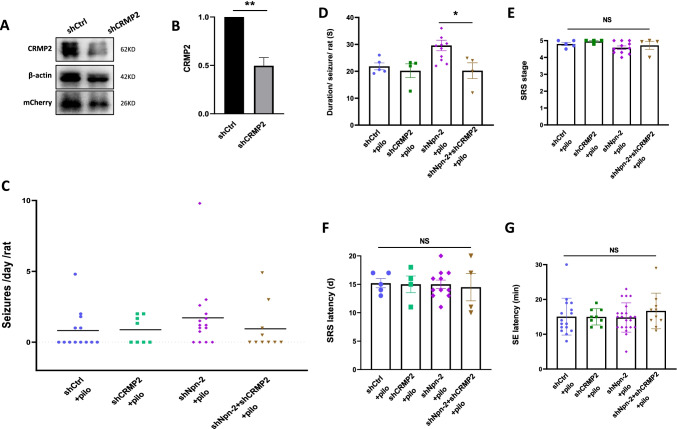
Fig. 9.
CRMP2 mediates Npn-2 function in regulating seizure activity. A CRMP2 knockdown validation in vivo. Fourteen days after intrahippocampal injection of shCtrl AAV or shCRMP2 AAV, rats were sacrificed for western blot analysis, and an effective knockdown of CRMP2 was observed. B Quantitation of CRMP2 in A, n = 3, **P = 0.0039. C Overview of SRS. Five out of 13 (38%) rats in shCtrl group and 4 out of 8 (50%) rats in shCRMP2 group developed SRS during the 21-day surveillance period post pilocarpine injection. Four out of 10 (40%) in shNpn-2 plus shCRMP2 group, while 11 out of 14 (73%) rats in shNpn-2 alone group developed SRS. D Mean duration per seizure. Seizure duration in shNpn-2 plus shCRMP2 group was 20.23 s, which was significantly less than the 29.59 s in shNpn-2 group (*P = 0.0459). E SRS stage. There was no significant difference in SRS stage among shCtrl group, shCRMP2 group, shNpn-2 group, and shNpn-2 plus shCRMP2 group (4.800 vs 4.950 vs 4.577 vs 4.718, P = 0.2579). F SRS latency. No significant difference in SRS latency was found among shCtrl group, shCRMP2 group, shNpn-2 group, and shNpn-2 plus shCRMP2 group (15.20 days vs 15.00 days vs 15.00 days vs 14.50 days, P = 0.9867). G SE latency. The SE latency of rats in among shCtrl group, shCRMP2 group, shNpn-2 group, and shNpn-2 plus shCRMP2 group was similar to each other (15.06 min vs 15.00 min vs 14.82 min vs 16.7 min, P = 0.7306). One-way ANOVA, post hoc Tukey test. Error bars represent SEM