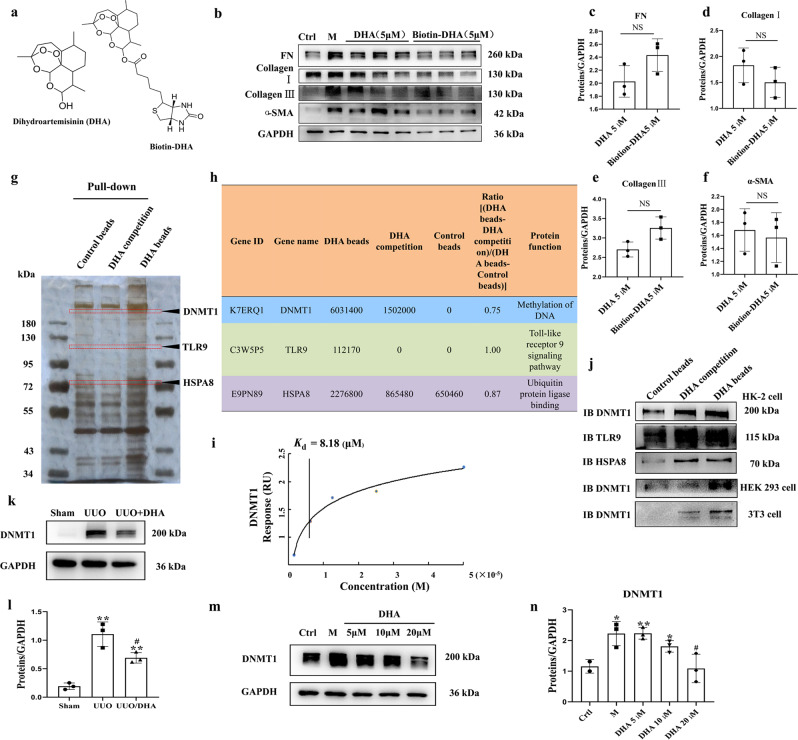
Fig. 2. DNMT1 was identified as the target of DHA.
a The chemical structures of DHA and the biotin-DHA analogs. b Expression of fibronectin, collagen I, collagen III and α-SMA in HK2 cells treated with TGF-β (10 ng/mL) in the presence or absence of DHA and Biotin-DHA for 48 h as assayed by Western blotting. c–f Quantification analysis of (b). g DHA target proteins were identified using pull-down technology coupled with shotgun proteomics. The HK-2 lysates were incubated with DHA beads or control beads, and then the proteins bound to the beads were resolved by SDS/PAGE, followed by silver staining. h The results of silver staining as analyzed by proteomics. i SPR analysis of DHA binding to DNMT1. j HK-2, HEK293, and 3T3 cell lysates were incubated with DHA beads or control beads, and the proteins bound to the beads were resolved by SDS/PAGE, followed by Western blotting. k Protein expression of DNMT1 from sham, UUO and DHA-treated UUO mice as assayed by Western blotting (three samples in each group). l Quantification analysis of (k). m Protein expressions of DNMT1 in HK2 cells treated with TGF-β (10 ng/mL) in presence or absence of DHA for 48 h as assayed by Western blotting. n Quantification analysis of (m). The results are the means ± SD of at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01 (compared with sham group or control group); #P < 0.05 (compared with the UUO group or M group).