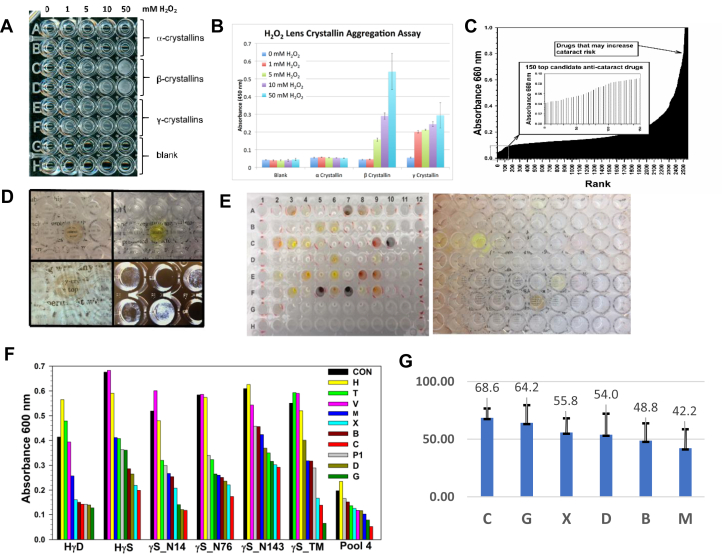
Figure 1.
Testing conditions for screening of drugs with potential anti-cataract activity.A, solutions of bovine lens crystallin fractions (2 mg/ml in 50 mM K3PO4 buffer) rich in β-crystallin and γ-crystallin become turbid when exposed to H2O2 at 37 °C up to 72 h. B, turbidity is quantified using absorbance at 450 or 600 nm. Note that α-crystallin-rich proteins are considerably resistant to heat denaturation. C, fitness plot ranking from highest to lowest for assessing turbidity inhibition potency of 2650 small molecules added at 500 μM concentration to gamma-crystallins exposed H2O2 (45 mM) at 37 °C for 24 h. The profile of the top most potent drugs is shown in the inset. Conceptually, compounds that suppress turbidity have anticataract activity, whereas compounds that increase it are cataractogenic. D, representative examples of turbidity suppression by three colored drugs allowing fine text read-through and visible protein aggregate suppression by dark field microscopy. E, a sublibrary of about 80 compounds (left) was retested at 150 μM concentration from which the best compounds were selected for further studies based on text read-through testing (right). F, to validate the initial screening results, top candidate compounds were screened for turbidity suppression of solutions of recombinant hCRYGD and hCRYGS, its deamidation mutants N14D, N76D, N143D, and the triple mutant TM. Drugs in 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) were hematoporphyrin (H), tetra sodium sulfate (T), V (avocadene), chaulmoogric acid (M), hexachlorophene (X), bixin (B), closantel (C), gambogic acid (G), dihydrogambogic acid (D) versus bovine α-crystallin (pool 1) and 10% DMSO as negative control (CON). G, bar graph shows the mean aggregation suppression score of the top six most potent drugs C, G, X, D, B, and M based on a composite of all screening data in bovine, HγD and HγS crystallins (F) and the extended data in B. Drugs C (closantel) and G (gambogic acid) emerged as the consistently most effective aggregation suppressors from 2650 compounds tested. HγD, human gamma D; HγS, human gamma S.