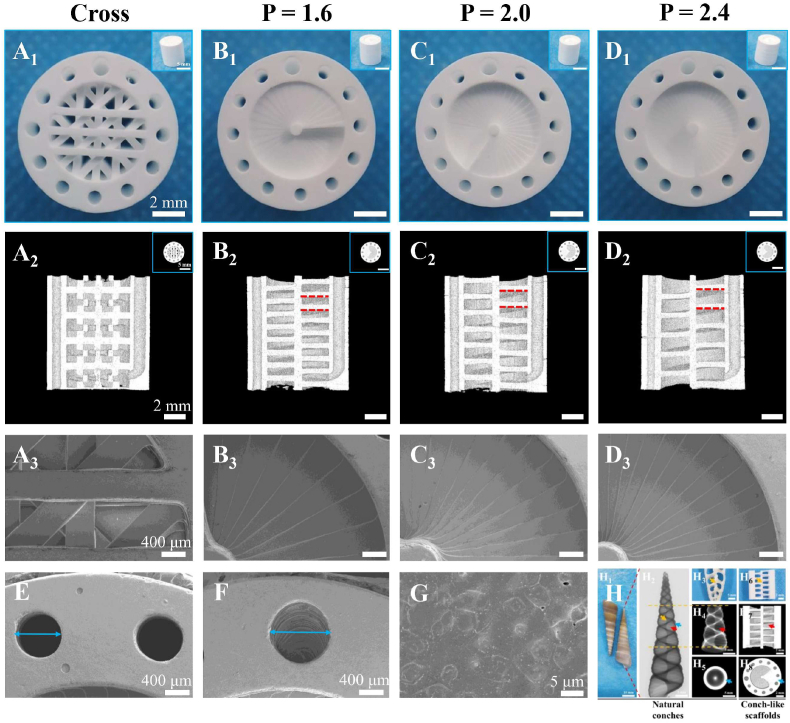
Fig. 2.
Structure and morphology characterization of the 3D-printed CL scaffolds and the natural conches. Digital photograph of the conventional cross-strut scaffolds (A1) and the CL scaffolds with varied pitches (B1-D1) (P = 1.6, 2.0 and 2.4 mm, D = 1.2 mm, N = 12) in vertical view (the inset figures showed the side-view digital photograph of corresponding scaffolds, scale bars = 5 mm), scale bars = 2 mm. (A2-D2) The sagittal Micro-CT reconstruction images of the scaffolds to show their spiral structure in the inner of CL scaffolds (the inset figures showed the transverse view, scale bars = 5 mm), scale bars = 2 mm. (A3-D3) The representative SEM images of scaffolds, scale bars = 400 μm. (E) SEM image for through macropores in the peripheral wall (Ф = 1.2 mm in model), scale bar = 400 μm. (F) SEM image for cell-seeding channel in the peripheral wall (Ф = 1.5 mm in model), scale bar = 400 μm. (G) SEM image for the surface of scaffolds, scale bar = 5 μm. (H) Structure and morphology characterization of natural conches, and the similarity in structure between the natural conches and 3D-printed CL scaffolds (P = 2.4 mm, N = 12, D = 1.2 mm). Specifically, digital photograph (H1) and Micro-CT image (H2) of the natural conches (turritella terebra), scale bars = 10, 5 mm. Digital photograph of the double sagittal section of the natural conches (terebra maculata), scale bar = 5 mm (H3). Sagittal section (H4) and transverse section (H5) images of the natural conches (turritella terebra) in H2, scale bars = 5 mm. Digital photograph of the double sagittal section of the 3D-printed CL scaffolds, scale bar = 2 mm (H6). Sagittal section (H7) and transverse section (H8) images of the 3D-printed CL scaffolds (P = 2.4 mm), scale bars = 2 mm.