Fig. 5.
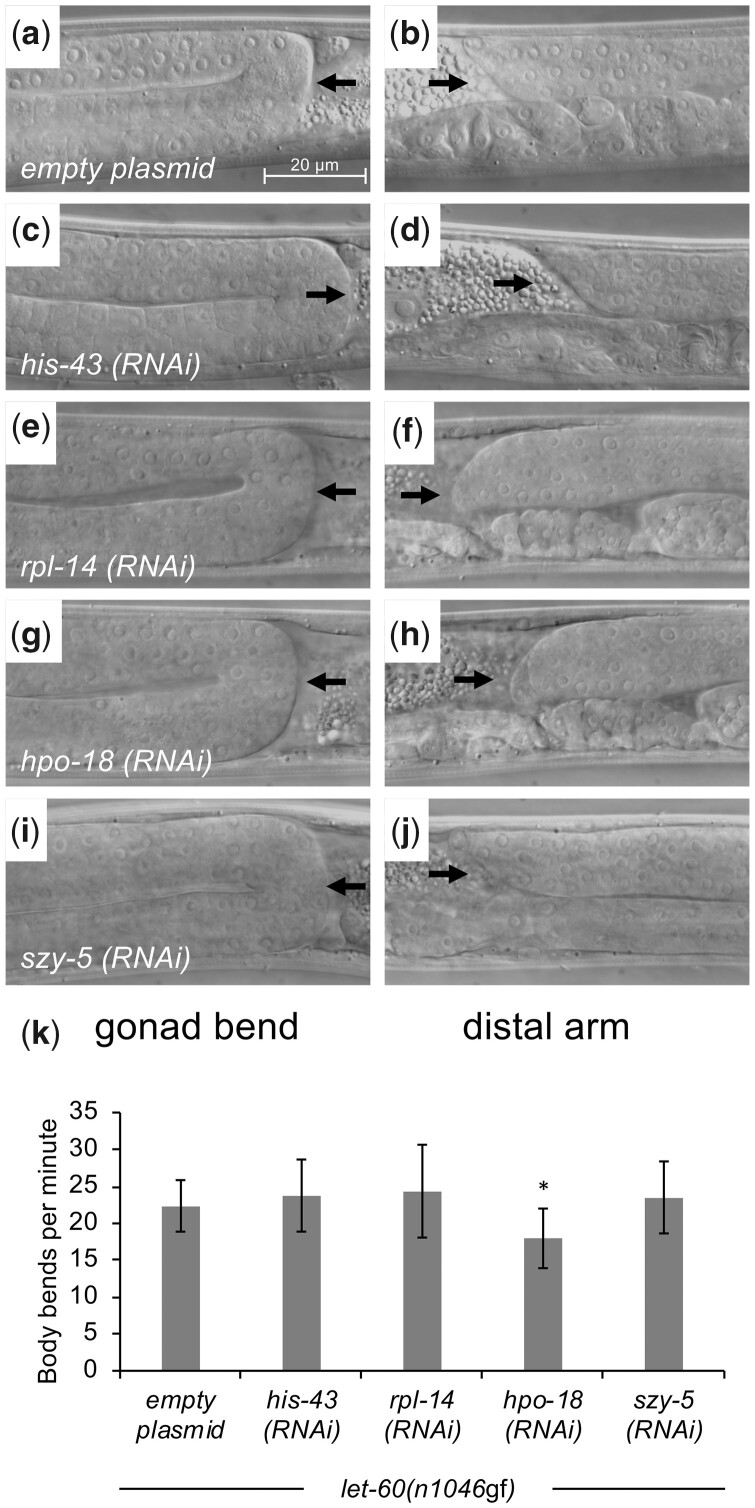
Gross gonad and muscle functions are maintained upon mesodermal-RNAi knockdown of identified genes. a–j) Hermaphrodite animals from CM2453 (mesodermal-RNAi strain) treated with RNAi under conditions that produce a phenotype were selected as L4s and evaluated for gonad morphology, including appropriate bending at the 2 ends of the animal, and presence of the distal ends in the middle of the animal, suggestive of normal somatic gonad anatomy and distal tip cell migration. RNAi knockdown of representative genes identified in the screen do not disrupt normal somatic gonad morphology. Black arrows in the figures from the left column indicate dorsal-to-ventral bend of gonad arm, while black arrows from the right column show presence of a distal gonad arm dorsal to the uterus. Representative animals shown, with n = 10 evaluated for each RNAi knockdown and no defects observed. k) Muscle function was evaluated using a locomotion (body bends per minute) assay. RNAi knockdown of representative genes generally does not alter muscle function, although knockdown of hpo-18 had a modest effect. n = 10 for each RNAi knockdown. Error bars correspond to standard deviation. Asterisks indicate statistically different from control (2-tailed t-test, *P < 0.05). Raw data provided in Supplementary tables.